What are Agile Requirements? In a landscape where companies seek ways to enhance their products and boost customer satisfaction, agile project management emerges as a powerful tool.
What is Agile Project Management?
Agile Project Management is an iterative and flexible approach to overseeing and delivering projects. It originated from Agile software development methodologies and emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
In Agile Project Management, regular communication and stakeholder involvement are important. This method encourages frequent reassessment and adaptation, making it ideal for projects where requirements are expected to evolve.
The focus is on delivering functional components or ‘increments’ at the end of each sprint, ensuring a continuous flow of value.
Moreover, Agile emphasizes the importance of a motivated team, providing the environment and support they need and trusting them to do the job.
This leads to higher team morale, better productivity, and a more successful project outcome.
Agile’s adaptability makes it applicable beyond software development, including in industries like marketing, event planning, and product development.
What are Agile Requirements?
In Agile methodologies, requirements take on a dynamic and adaptive nature. Unlike traditional project management approaches, where requirements are fixed and detailed upfront, Agile requirements are fluid and responsive.
- Collaborative Shaping: Agile requirements are collaboratively shaped throughout the development process
- Adaptability: Teams can adjust to changing circumstances and priorities, a crucial aspect in Agile development
- Emphasis on Flexibility: Agile methodologies prioritize delivering incremental value and prompt responses to customer feedback
- Expression through User Stories: Agile requirements are often expressed through user stories, capturing end-users perspectives and needs
- Prioritization by Business Value: User stories are prioritized based on business value, ensuring a focus on the most crucial features
- Iterative and Incremental Nature: Agile requirements follow an iterative and incremental approach, allowing real-time adjustments.
- Continuous Improvement Cycle: The nature of Agile requirements fosters a continuous improvement cycle within the development process.
- Effective Accommodation of Changes: This approach accommodates changes effectively, enhancing overall responsiveness and project success in Agile methodologies.
Benefits of Agile Requirements
Agile requirements refer to managing and documenting project requirements within the Agile framework, a flexible and iterative methodology for software development and project management.
Here are some benefits of Agile requirements:
◉ Adaptability to Change
Agile requirements prioritize flexibility, allowing teams to adjust project priorities and features as needed. This ensures the project can easily respond to changing market conditions, customer feedback, or business requirements without significant disruptions.
◉ Continuous Customer Involvement
Agile encourages ongoing collaboration with customers, involving them in the development process from start to finish. This iterative engagement ensures that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations, resulting in higher satisfaction and a more successful end product.
◉ Incremental Value Delivery
Agile requirements focus on delivering small, valuable increments of functionality in each iteration. This approach allows teams to release usable features sooner, providing stakeholders with tangible benefits early in the project and enabling quicker time-to-market.
◉ Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Agile methodologies emphasize open communication and collaboration between the team and stakeholders. This ensures a shared understanding of project goals, reduces the risk of miscommunication, and fosters a more productive and cohesive working environment.
◉ Risk Mitigation
Agile’s iterative nature allows teams to identify and address potential risks early in development. By breaking down the project into smaller, manageable increments, teams can proactively manage challenges, reducing the overall risk and ensuring a smoother project flow.
◉ Improved Product Quality
Agile requirements promote continuous testing and feedback loops throughout development. This iterative testing helps identify and address issues promptly, contributing to a higher overall product quality. By addressing concerns early, teams can deliver a more reliable and robust end product.
How to Collect Agile Requirements?
Efficient strategies for gathering Agile requirements ensure alignment providing a streamlined and effective process.
Stakeholder Collaboration and Goal Determination
Engage in collaborative discussions with each project team member, including developers, customers, and stakeholders. Establish a shared goal by clarifying the ideal end state and responsibilities for everyone involved.
This ensures a cohesive understanding of the project’s purpose and helps the team move forward with a unified vision. Work together for each sprint or feature to define clear objectives and expectations.
User Stories and Narrowing Requirements
Utilize user stories to capture specific functionalities from an end-user perspective. Break down these stories into clear, concise one- or two-page documents, emphasizing the most crucial information.
Many Agile tools and software systems provide a ticketing structure that facilitates the organization of requirements. Project managers can then rearrange and prioritize these requirements based on their importance and changes, providing a clear order for their release.
Iteration and Continuous Refinement
Engage in iterative cycles to continually refine and adjust requirements. Regularly review and reassess the gathered requirements to accommodate changing project needs or evolving priorities. This iterative approach allows for flexibility and adaptability, ensuring that the requirements remain aligned with the dynamic nature of Agile projects.
Finalization and Unique Identifiers
Once the team has narrowed down and established requirements, finalize them by assigning unique identifiers. These identifiers can coherently integrate requirements into schedules, project plans, or Agile boards. Consider creating a system where each requirement has a clear reference point for tracking progress and implementation throughout the workflow.
Review with Product Teams and Leadership
Before executing tasks based on the finalized requirements, conduct a thorough review with product teams and leadership. Ensure that everyone agrees on the requirements and aligns with overall project goals.
This step helps mitigate misunderstandings, validates the clarity of requirements, and secures the necessary buy-in from key stakeholders before proceeding with task execution.
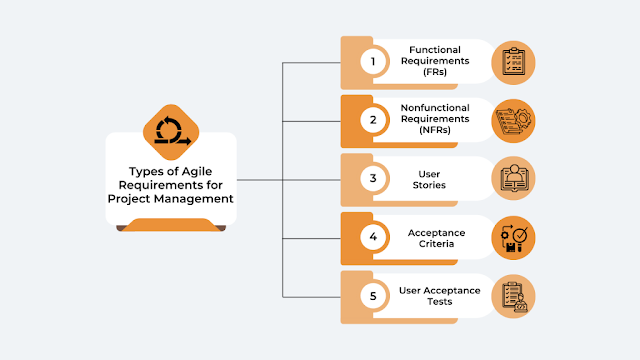
Types of Agile Requirements for Project Management
Identifying Agile requirements in project management is crucial for shaping the end product and setting performance benchmarks. Here are some common types of Agile requirements integral to effective project management.
Functional Requirements (FRs)
Agile functional requirements pinpoint specific functions or features the final product must possess. Teams utilize these to outline steps for product development, establish goals, and set benchmarks to track progress.
Examples include features like a customer feedback form on a landing page or a searchable database for past invoices.
Nonfunctional Requirements (NFRs)
Nonfunctional requirements, or quality attributes, define the expected performance of a solution. Areas such as usability, security, reliability, and overall system performance fall under NFRs.
These requirements ensure the product behaves as intended, protecting against unauthorized access, ensuring reliability, and measuring user satisfaction.
User Stories
Agile teams express requirements from an end-user perspective through user stories. These stories help assess feature importance, break down complex functionalities, and guide product development to meet user needs.
These stories facilitate communication by articulating the end-user perspective, fostering a cohesive approach to feature prioritization and development alignment with user needs.
Acceptance Criteria
Acceptance criteria define how to test or measure the success of a user story. These criteria establish metrics to assess project success, such as improvements in customer retention or specific speed benchmarks for product dispatch.
Following the golden rule of goal setting, like SMART goal methodology, acceptance criteria ensure specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based requirements.
User Acceptance Tests
User acceptance tests provide scenarios for testing specific product or service features. These tests help teams and clients understand how features work and verify if solutions meet customer needs.
For instance, a user acceptance test for a confirmation email feature may include visiting the registration website, filling out a form, and confirming email receipt.
Here is a detailed explanation of the same:
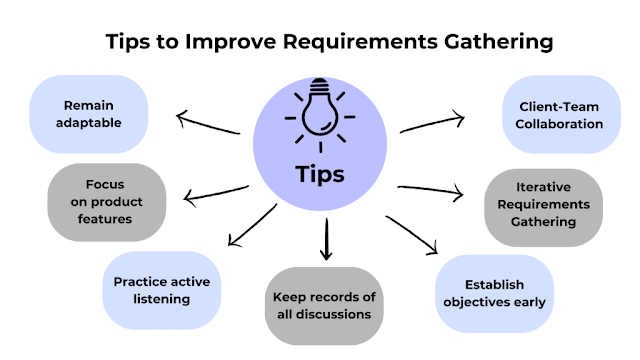
Client-Team Collaboration
Effective requirements gathering necessitates close collaboration between the client and the development team. Encourage open communication channels involving key stakeholders from the client side to ensure a comprehensive understanding of their needs, expectations, and project goals.
Iterative Requirements Gathering
Acknowledge that requirements gathering is an iterative process. Embrace ongoing feedback loops to refine and adjust requirements as the project progresses. Iterative approaches accommodate changing priorities, allowing for a more flexible and adaptive development cycle.
Establish objectives early
Clearly define project objectives from the outset. Having a well-defined scope and understanding of project goals helps streamline requirements gathering. This early clarity guides the team in prioritizing and aligning features with the overarching project vision.
Keep records of all discussions
Maintain detailed records of all discussions during requirements gathering. Documentation serves as a valuable reference, preventing misunderstandings and providing a historical context for decisions made throughout the project. This ensures consistency and clarity in the development process.
Practice active listening
Active listening is crucial during requirements gathering. Encourage team members to attentively absorb client input, ensuring a thorough understanding of their perspectives. This practice facilitates more accurate and comprehensive requirement identification.
Focus on product features
Concentrate on identifying and understanding the desired product features. Collaborate with stakeholders to prioritize features based on business value and user needs. This focus ensures that the development effort aligns with delivering the most impactful and valuable functionalities.
Remain adaptable
Acknowledge that requirements are subject to change. Foster an adaptable mindset within the team to accommodate evolving project needs. This flexibility allows for responsive adjustments to requirements, aligning with changing business conditions or client expectations.
Source: invensislearning.com





.jpg)