Curious about how Agile teams effectively communicate and collaborate? Dive into the world of Information Radiators with our blog—‘What is an Information Radiator in Agile?’ Uncover the key concepts behind Scrum and Kanban boards, explore their origins, understand the benefits, and learn how to create your Information Radiator.
If you’ve ever wondered about the visual aspects of Agile methodologies and how they enhance team efficiency, this blog is your go-to guide.
Let’s demystify the power of Information Radiators in Agile together.
What is an Information Radiator in Agile?
An information radiator in agile development, visualizes an ongoing project, offering insights into a team’s advancements. It undergoes regular updates as developers navigate through different phases of design and launch processes.
The primary objective of an information radiator is to provide easily accessible information for software teams, helping them maintain focus on critical tasks.
These visual aids can take the form of hand-drawn charts or electronic displays and encompass various elements such as:
1. Scrum Board
Scrum boards are organizational tools within the scrum framework, allowing teams to segment projects into one to four-week sprints. Tasks are documented on sticky notes or cards and progress through columns like “to do,” “in progress,” and “done.”
2. Kanban Board
Kanban boards are visual tools aligning with the Kanban style of agile development. They consist of columns representing different workflow stages. Tasks are listed on cards or sticky notes, progressing through columns based on their stage. Priority is usually indicated by positioning tasks at the top and moving through the chart until completion.
3. Calendar
Maintaining a strict release schedule is a key priority for agile development teams. Many information radiators incorporate calendars to depict the planned schedule for project completion, aiding team members in adhering to deadlines.
4. Incident Reports
Throughout the development process, teams may encounter obstacles or incidents that impede progress. Tracking these events is crucial for preventing recurrence and maintaining a detailed project record.
Incident reports are commonly integrated into information radiators, featuring a list of incidents along with their dates and times.
5. Other Elements
Comprehensive information radiators in Agile go beyond basic components. In addition to calendars, incident reports, and task boards, they may include various graphics reflecting project status.
This could involve test records, progress charts, obstacle boards, team velocity reports, or the team’s continuous integration status. The goal is to provide a holistic overview that empowers teams to monitor progress and stay on course.
Origin of Information Radiators
In the 1980s, the concept of “visual control” emerged within the Toyota Production System, laying the groundwork for what would later be known as “information radiators.”
This approach, rooted in Lean manufacturing principles, aimed to create a visual workplace where information about production processes was readily available, aligning with the core tenets of transparency and efficiency.
Fast forward to 1999, and Kent Beck, in his influential work “Extreme Programming Explained,” introduced the term “Big Visible Chart” to underscore the significance of prominently displayed charts in conveying project information. Notably, Beck later credited Martin Fowler for coining the term.
Finally, in 2001, Alistair Cockburn coined the term “information radiator” as part of an extended metaphor that drew parallels between the movement of information and the dispersion of heat and gas. T
This symbolic framework emphasized the crucial role of making project information visible and easily accessible, reflecting the evolutionary journey from visual control in manufacturing to the information-centric practices embedded in agile methodologies.
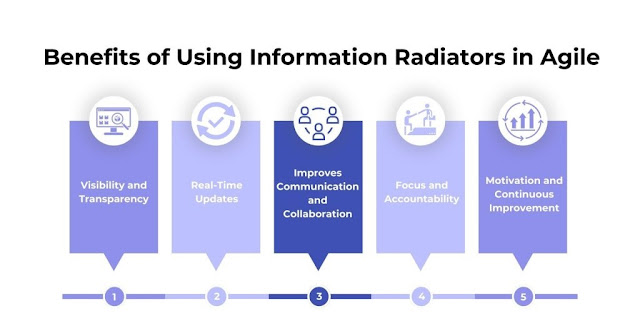
Benefits of Using Information Radiators
The use of information radiators in project management and agile development provides several benefits that contribute to improved communication, collaboration, and overall project success.
Some key advantages include:
- Visibility and Transparency: Information radiators visually depict project status, fostering shared understanding, minimizing misunderstandings among team members, and promoting goal alignment
- Real-Time Updates: Information radiators, with frequent updates, provide real-time insights, empowering teams to make informed decisions and maintain agility in response to evolving project requirements
- Improves Communication and Collaboration: Task boards and charts facilitate efficient team communication by conveying task status and priorities, fostering collaboration through a centralized coordination point
- Focus and Accountability: Information radiators display tasks and progress, reinforce focus on project goals, and foster visual accountability that motivates team members to meet deadlines and take ownership of responsibilities
- Motivation and Continuous Improvement: Visualizing progress on information radiators boosts team morale, and the representation of project metrics fosters a culture of continuous improvement in the development process
In summary, information radiators offer a range of benefits that contribute to a more transparent, efficient, and collaborative project environment, aligning well with agile development principles and effective project management.
How to Create an Information Radiator?
Creating an effective information radiator in Agile involves defining clear objectives, selecting appropriate visual elements, regular updates, strategic placement, and fostering team engagement for enhanced communication and project visibility.
Here is an information radiator that involves several key steps:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Clearly outline the goals and information you want the radiator to convey. Whether tracking project tasks, displaying metrics, or visualizing team progress, defining objectives ensures the radiator serves its purpose effectively.
2. Select Appropriate Visual Elements
Choose visual elements that align with your objectives and resonate with your team. This could include task boards, charts, or calendars. Opt for elements that convey information clearly and easily understandable for effective communication.
3. Regularly Update Information
Commit to keeping the information radiator current by regularly updating the displayed data. Real-time updates ensure the team has the latest insights, fostering agility and informed decision-making.
4. Prominent Display Location
Place the information radiator in a visible and easily accessible location within the team’s workspace. A prominent location encourages regular engagement, ensuring team members naturally refer to the displayed information during their daily activities.
5. Encourage Team Interaction
Cultivate a collaborative environment by encouraging team members to actively engage with the information radiator. Whether updating task statuses or providing feedback, promoting interaction ensures that the radiator becomes a dynamic and integral part of the team’s workflow.
By following these steps, you can create an information radiator that enhances communication, collaboration, and project visibility within your team.
Information Radiator Vs. Information Refrigerator
The term “Information Radiator” refers to a dynamic and visible display utilized in agile project management, typically presented through charts, boards, or electronic screens. Its primary objective is to enhance transparency and facilitate communication within a team by offering real-time updates on project status and goals.
This dynamic approach aims to foster collaboration, ensuring the team remains well-informed for agile decision-making and adaptability.
Conversely, the term “Information Refrigerator” lacks recognition as a professional concept. If interpreted playfully, it could hypothetically suggest a static or cold storage of information, implying a less dynamic or interactive means of conveying project details. However, it is crucial to clarify that “Information Refrigerator” does not hold standard usage within project management or technology.
Kanban Board Vs. Scrum Board
Kanban boards and Scrum boards, fundamental to agile project management, diverge in foundational frameworks and methodologies. Kanban, associated with a continuous and efficient workflow, needs more flexible roles or prescribed timeframes.
Tasks progress fluidly through stages, accommodating dynamic priorities. The board emphasizes complete visibility, promoting an uninterrupted flow of work.
In contrast, the Scrum board is integral to the Scrum framework, organizing work into fixed-length sprints. Specific roles and ceremonies are defined, such as the Product Owner, Scrum Master, Sprint Planning, Daily Standups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
The Scrum board showcases tasks for the ongoing sprint, providing structure with columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done,” but offers less flexibility within defined sprint durations. The choice between Kanban and Scrum depends on project requirements, team preferences, and the nature of the work undertaken.
Source: invensislearning.com






0 comments:
Post a Comment