A Brief Understanding of COBIT 5!
Developed by ISACA, COBIT 5 helps businesses to create frameworks, and organize and implement strategies for information management and governance.
The COBIT 5 framework simplifies a set of managerial procedures with each procedure carefully explained together with process inputs and outputs, process objectives, key process activities, elementary maturity model, and performance measures. It additionally gives a lot of recommended best practices for organizational management and control procedure of data frameworks and technology with the point of adjusting the business to information technology. COBIT is probably the most holistic framework that is recognized internationally for achieving organizational information technology goals and objectives.
What is COBIT 2019?
The framework addresses the latest trends, technologies, and security needs for enterprises including other IT management frameworks such as ITIL, CMMI, and TOGAF as it makes an incredible choice to unify processes across an entire organization. Like COBIT 5, It also emphasizes specifically security, risk management, and information governance.
What does COBIT 2019 Include?
In COBIT 2019, new concepts and terminology have introduced the COBIT Core Model, which includes 40 governance and management objectives for establishing a governance program. The framework is intended to give organizations greater adaptability while customizing an IT governance procedure. Like any other framework related to IT, COBIT aligns the business goals and IT goals by establishing links between the two and creating a process that can help bridge a gap between specific silos within IT using their framework or standard.
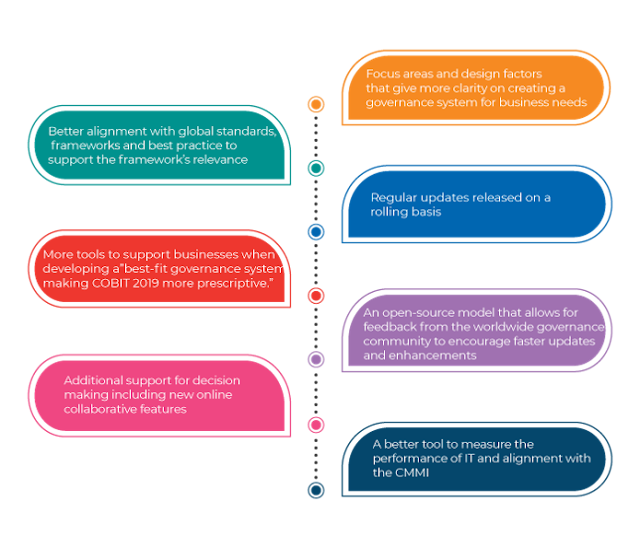
According to the ISACA, COBIT 2019 was updated to include:
It additionally hosts “focus area” concepts that define specific governance topics and issues, which can be addressed by management or governance objectives. A few instances of these focus areas incorporate small and medium ventures, cybersecurity, digital transformation, and cloud computing. Focus areas will be included and changed as required depending on the trends, research, and feedback. There’s no restriction on the number of focus areas that can be incorporated into COBIT 2019.
COBIT 2019 Certification
Are you a certified professional in COBIT 5 through ISACA or in the middle of getting your certification? Are you already an accredited professional in COBIT 5 through ISACA or in the middle of getting your certification? The COBIT 5 certification course does not expire; ISACA will continue to support the accreditation and delivery of COBIT 5 training and certifications, along with COBIT 2019.
Certifications for COBIT 2019 include:
1. COBIT Bridge Workshop: A one-day course that covers the concepts, models and key definitions in COBIT 2019 with a heavy focus on the differences between COBIT 5 and COBIT 2019.
2. COBIT 2019 Foundation Exam: Prepares attendees for the COBIT 2019 Foundation certificate exam, covering the “context, components, benefits and key reasons COBIT is used as an information and technology governance framework.” You’ll be able to earn your certificate in COBIT 2019 Foundation after a two-day course from an accredited training provider.
3. COBIT 2019 Design and Implementation Exam: this certification will launch in April 2019 and will cover designing a tailor-made best-fit governance system using COBIT.
Design Factors in COBIT 2019!
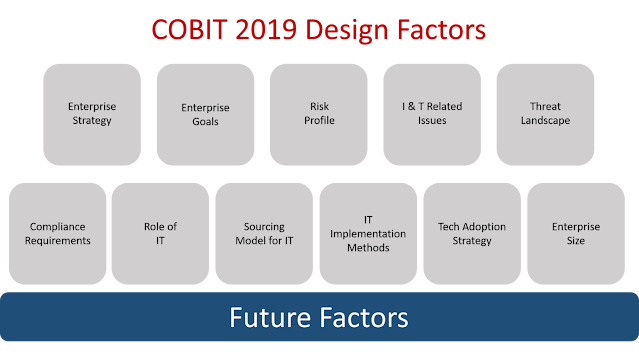
Eleven design factors are introduced in COBIT 2019. The design factors influence the sort of governance system your organization needs and elevates the required capabilities. The new design factors can also influence the importance of one or more components or require specific variants.
The new design factors are shown in the image below:
COBIT 2019 Core Publications
Good governance is a vital element of strategy formulation and business transformation success, and COBIT 2019 can help chart that path forward. Below are the four core publications.
COBIT 2019 Framework: Introduction and Methodology
The new COBIT 2019 framework explains the governance principles and provides key concepts and examples. This guide also offers the structure of the overall framework, including the COBIT Core Model.
COBIT 2019 Framework: Governance and Management Objectives
This new publication provides a detailed description of the COBIT Core Model and its 40 governance/management objectives. Each objective is defined and coordinated with the related process, enterprise goals, and governance and management practices.
COBIT 2019 Design Guide: Designing an Information and Technology Governance Solution
The new design guide offers prescriptive on how to put COBIT to practical use and how to tailor a governance system to the enterprise’s unique circumstances and context, defining and listing various design factors. This guide also recommends workflows for creating the right-sized design for your governance system.
COBIT 2019 Implementation Guide: Implementing and Optimizing an Information and Technology Governance Solution
The Implementation Guide provides a roadmap for continuous governance improvement. The COBIT implementation is more practical and custom-tailored to specific governance needs.
The Guide provides a roadmap for continuous governance improvement. The COBIT implementation is more practical and custom-tailored to specific governance needs.
Source: invensislearning.com