Project management methodologies have essential roles in how you govern your project. Until a few years back we used to have one popular project management methodology, which is the traditional project management methodology or waterfall.
This methodology was useful for construction types of projects where you have a well-defined scope; however, IT projects had trouble with this project management approach because these projects had continuous changes and the waterfall method was not suited for projects with changing requirements.
So project managers needed new methodologies to help deal with changing requirements. Consequently, Agile methodologies came, and afterward, many more new more project management approaches followed.
In today’s post, I will introduce you to ten popular project management methodologies.
Project Management Methodologies
A project management methodology is a set of guidelines and best practices that help you to complete your project efficiently with less obstruction.
Every project is unique and you need the right methodology for your project.
The project management framework evolved from a traditional approach to Agile, resulting in significant changes in the way we carry out the project activities.
Project management approaches affect the culture of the organization and the project team. You need to understand the culture to work seamlessly with your team.
Here are the top ten project management methodologies used by organizations to complete their projects:
1. Waterfall
2. Scrum
3. Disciplined Agile
4. SaFE (Scaled Agile Frameworks)
5. DSDM (Dynamic Systems Dev. Method)
6. LeSS (Large Scale Scrum)
7. Scrum of Scrum (SoS)
8. XP (eXtreme Programming)
9. Kanban
10. Lean
#1. Waterfall
This is the most popular project management methodology. Here you have a well-defined scope and activities are planned in sequence. You invest a lot of effort into collecting requirements and then developing the project management plan. Once all plans are developed, baselines are created, you get them approved and follow them religiously.
Changes in the project management plan or baseline are not easy. All change requests go through a lengthy process to get approved. After the approval, you will update your plans and baselines.
Changing requirements in this project management approach are difficult and costly. All change requests go through a time-consuming change management process.
Time and Risk Increase WIth Progress
The waterfall methodology is impracticable for a dynamic environment where requirements keep on changing.
The scope in a waterfall is fixed, unlike Agile where changing customer needs is built into the methodology. Feedback in agile is continuous, whereas, in the waterfall method, it’s at the point of validating scope. You can miss defects during the product development, and correcting them at a later stage will be time-consuming and costly.
But in Agile, changes are part of the framework. Customers can request changes at any time, and finding defects is easier because of frequent demos.
In waterfall, quality control activities are carried out throughout the execution phase, unlike test-driven Agile projects where you build in quality with automated testing as the project progresses.
The waterfall method is suitable for well-understood projects with stable requirements.
#2. Scrum
Scrum is one of the most popular Agile methodologies. It guides the team on iterative and incremental product development.
While a traditional project management methodology works with fixed requirements and optimizes around time and cost, Scrum, on the other hand, fixes time (via time boxes) and cost (via prioritizing the product backlog for a potentially shippable delivery) to optimize changing customer requirements through collaboration and frequent feedback.
Scrum is an adaptive methodology to develop the desired product.
Scrum Events

N.B.: The sprint is a time-boxed activity to complete the work. The sprint ends with a sprint review and then a retrospective. The product backlog may change, but once the sprint is planned, any new feature is sent to the product backlog and prioritized for the next sprint. A sprint normally lasts two weeks.
During the sprint, daily standups last for 15 minutes where each member tells the team what they did yesterday, what they plan to do today, and what is getting in their way. This is where the scrum master removes impediments.
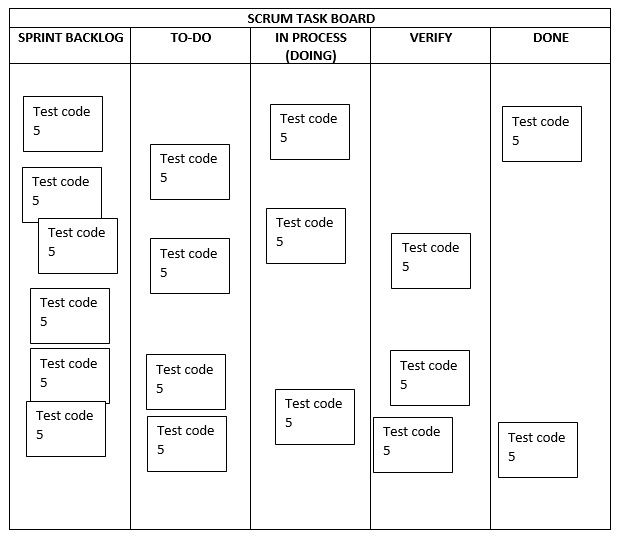
How does the scrum track progress in a sprint?
The team uses visible information radiators such as burndown charts and task boards to track the progress.
#3. Disciplined Agile
This is an upgraded version of Agile. It combines the freedom of choice and suitability with proper guidance on narrowing choices. It is characterized by the freedom to choose your way of working (WoW).
Disciplined Agile is context-dependent. It is about tailoring what works for you. It blends Scrum, SaFE (Scaled Agile Frameworks), Traditional (waterfall) approach, Kanban, eXtreme Programming, etc. It is an Agile optimization tool that can be used to extend agility from the team to the organizational level.
It accelerates value delivery, which can help customers test the product in the market quickly.
The Disciplined Agile (DA) has seven principles:
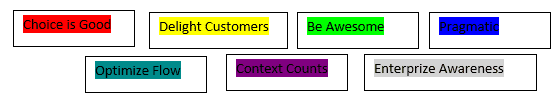
1. The choice is Good: You have to choose the best-fit technique for your processes/situation. You have to understand all choices and trade-offs of selecting a particular choice.
2. Delight Customers: The customer is the center of everything, whether internal or external. You have to make them happy. If you don’t delight them, someone else will and the customer will move elsewhere.
3. Be Awesome: Be awesome with what you do. If you are awesome, the client will love working with you.
4. Pragmatism: It implies doing what works, not what is usual. If something works best even in a traditional project approach, adopt it. Be as effective and efficient as possible.
5. Optimize Flow: Continuous flow of task/work by using Kanban. Your organization may have a complex flow system but you have to adapt to it. Ensure that communication is smooth between your team and the organization or even within different teams in your organization.
6. Context Counts: We all are unique and so is the organization’s culture. Understand the context and evolve with an effective strategy for the situation you face.
7. Enterprise Awareness: Ensure that the team is aware of their organization. It motivates them to align with the organization’s objectives and they will contribute to achieving larger goals.
DA uses six different life cycles, the life cycles are:
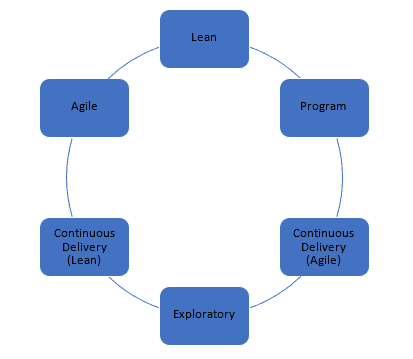
You can choose the best fit for your needs.
DA’s process tailoring workshops help your team understand the importance of working together. It includes selecting a lifecycle, walking through the process goals one at a time, addressing the decision points, and deciding roles and responsibilities.
DA has four phases: Inception, Construction, Transition, and Deployment.
As shown in the table below, these phases have 21 process goals:
Each process goal links to a decision point that further branches to various ways of achieving the goal.
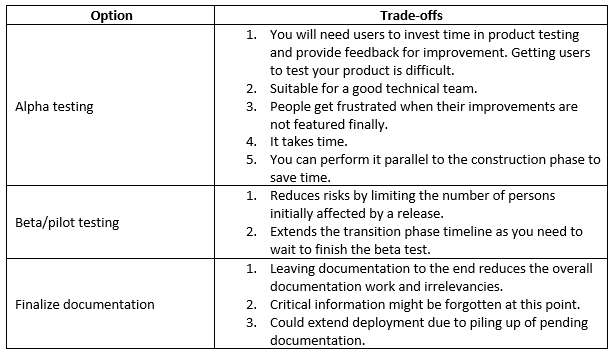
For example, assume you want to ensure production readiness.
DA believes business agility comes from freedom, not frameworks. So, it combines all known frameworks such as Lean and Scrum to eXtreme Programming and provides you with choices to select and deliver the consumable solution (not working software) to the market quickly.
Disciplined Agile helps you choose the best agile solution for your situation.
While Agile produces working software, DA produces a consumable solution. A consumable is a usable product that is ready to be deployed to the market.
In summary, Disciplined Agile deals with decisions you need to consider, the options available to you, and the trade-offs associated with these options. You make your choice.
This helps products get released to the market sooner.
Further on the example above, let’s consider the trade-offs for each option.
#4. SaFE (Scaled Agile Frameworks)
Here you take the lean and Agile approach from team level to enterprise level. It is about transition and bringing different agile teams together. To avoid challenges, large framework implementation requires a systematic approach to incorporate best practices.
SaFE helps in organizing several agile teams. Large companies like Microsoft and Ericsson have adopted the scaled agile approach.
Before we discuss SaFE any further, let us understand Agile methodology.
Agile methodology is flexible compared to traditional project management methodology and adapts to changing needs against a pre-planned approach. It provides customers with a minimum viable product (working software) as early as possible.
Agile is iterative and allows changing needs and dynamic environment realities. It breaks functional silos and pulls talent from each function into teams to achieve collaboration and coordination.
If your organization is intending to scale agile from team to enterprise-level, they must assess the fitness level of the team and its culture, including:
◉ Leaders with clear vision.
◉ Changes are welcomed and must be anticipated.
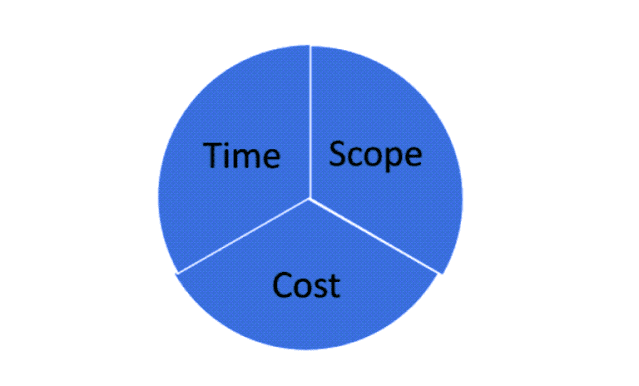
◉ Time and cost are fixed, but the scope is flexible.
◉ Stakeholders’ interest in working software components.
◉ Active customer participation.
The above conditions are typical agile requirements. Since the organization is adopting an agile approach, the team’s mindset must be agile to follow an agile framework.
Choosing an agile framework to scale depends on some factors, such as:
◉ The number of agile teams in the organization.
◉ The company strategy and the impact of agile practices.
◉ Average size and complexity of agile projects.
◉ Critical success factors for the transition.
These factors are better described in the ten principles of SaFE, which are:
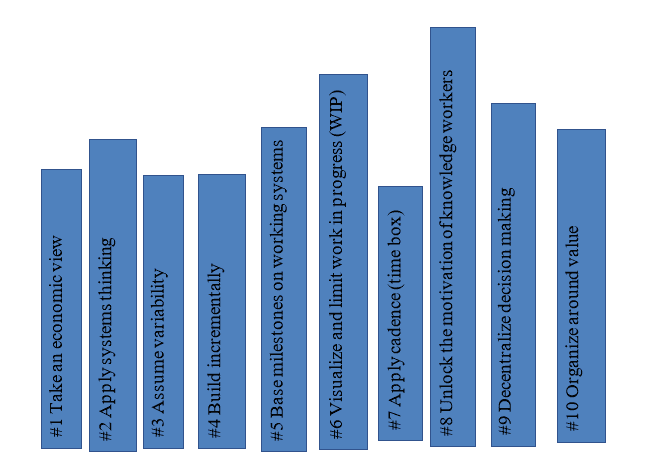
SaFE pioneered the Agile Release Train (ART) concept to organize teams around a value stream. They align teams (remember, scaled agile deals with several agile teams) to a shared business objective. A value stream is a set of actions that create customer value.
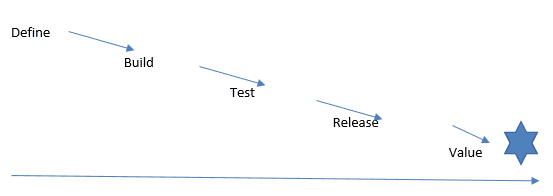
The term train is used to show interconnection. The figure below shows agile teams 1, 2, and 3 aligned on a value stream for a desired solution/feature.
T1, T2, and T3 are agile teams, while S-is the solution or the value. The value stream is the movement from design through build, test to deploy.
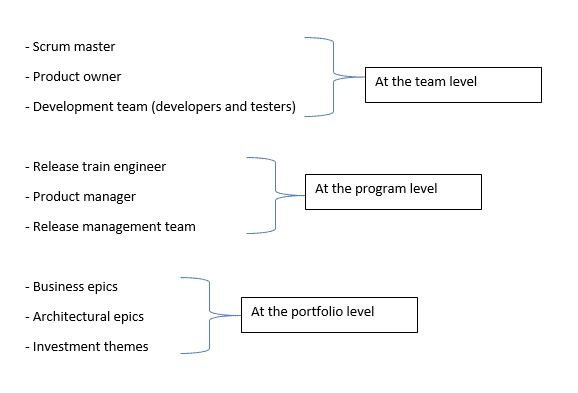
Some roles in SaFE are:
#5. Dynamic System Development Method (DSDM)
Agile and Kanban are subsets of lean and DSDM. DSDM is a framework applicable to constraint-driven projects where constraints such as cost, time, and quality are fixed, while scope (functionality/features) can change.
Its principles comply with agile such as collaboration, continuous and clear communication, iterative development, and delivery on time.
DSDM has eight principles:
1. Focus on the business needs. Every project decision must be in sync with high-level business value.
2. Deliver on time-timebox project tasks, focus on business priorities.
3. Collaborate and build a one-team culture for increased understanding, greater speed, and shared ownership.
4. Never compromise quality. Test early and continuously. Agree with the quality level from the outset.
5. Build incrementally from a firm foundation. This implies that a good understanding is required before building a solution.
6. Develop iteratively to embrace changes from feedback.
7. Communicate continuously and clearly. Aim for honesty and transparency in all communication.
8. Demonstrate control-make plans and projects visible to all using, for example, Gantt charts and task boards.
Roles in DSDM
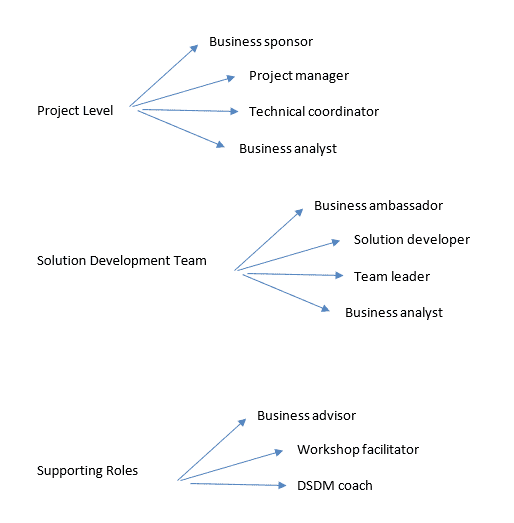
DSDM facilitates workshops. This helps engage stakeholders in solving a problem or developing a plan. The business owner, team lead, etc., can request this workshop.
The workshop is moderated by a neutral individual called the facilitator. The neutrality of the facilitator is important for a better outcome or workshop.
#6. Large Scale Scrum (LeSS)
LeSS is scrum extended to different scrum teams. It is a scrum applied to large-scale development. Here you still retain the basic attributes of a scrum, such as:
◉ Teams work on their sprints concurrently.
◉ One product owner handles the team.
◉ Teams are co-located.
◉ The teams work with one definition of done.
◉ One potentially shippable product from all the teams.
◉ One sprint for all.
◉ One product backlog for all, but each team has its own sprint backlog.
LeSS Principles
◉ Systems thinking: Everyone in the organization should focus on the whole product. They should know that there is no value in separate parts but integrated parts. It helps break silos, has a long-term team view, finds root cause solutions, and has fewer impediments. The team needs to understand the impact of their actions on the surrounding environment.
Other principles are
◉ Transparency
◉ Customer-centric
◉ Lean thinking
◉ More with LeSS (Large Scale Scrum)
◉ Continuous improvement
◉ Queuing Theory (reducing batch sizes to shorten delivery time)
◉ Empirical process control
#7. Scrum of Scrum
This project management methodology is useful when work from several scrum teams needs to be coordinated. Representatives from each scrum meet to coordinate their work. These representatives are referred to as “Ambassadors.”
The meeting is similar to the daily stand-up meeting where each representative reports completed work, the next assignments, and impediments. This meeting (Scrum of Scrums) aims to ensure smooth coordination of work.
This Scrum of Scrum can further extend to the Scrum of Scrums of Scrums depending on project size; the principle for coordination is the same.
Scrum of Scrum is also called meta-scrum. The duration of a scrum meeting is about 15 minutes. This is still retained at the Scrum of Scrum meetings.
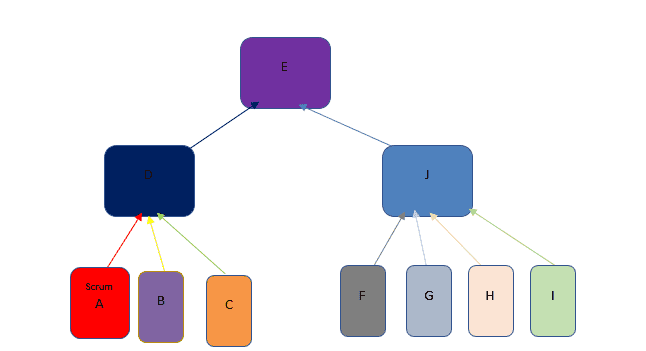
A, B, and C are scrum teams with one ambassador attending D, a Scrum of Scrums.
Similarly, J is the Scrum of Scrums of scrum teams F, G, H, and I.
The ambassadors of Scrum of Scrums D and J meet at E, Scrum of Scrums of Scrums.
It helps to ensure that the scrum teams fit together and operate cohesively.
#8. Extreme Programming (XP)
It started in 1996 when Chrysler Corporation embarked on a payroll restructuring program, the C3 (Chrysler Comprehensive Compensation) system. Their development team adopted a way of working that metamorphosed into Extreme Programming.
Extreme Programming (XP) has an agile mindset based on values, principles, and ways of working. XP is the foundation of excellent software development.
This is like refining, where you aim to get the purest product. Quality is at its peak. It requires repeated cycles of testing and refactoring.
The core values of Extreme Programming are Communication, Courage, Respect, Simplicity, and Feedback.
Extreme Programming has four practice areas: organizational, technical, planning and integration. These areas require primary practices, which are necessary for secondary (corollary) practices.
In the figures below, the practice areas are depicted with their corresponding primary and corollary practices. Red, yellow, and blue (primary colors) represent the primary practices, while secondary colors (orange, green, purple) represent the corollary practice.
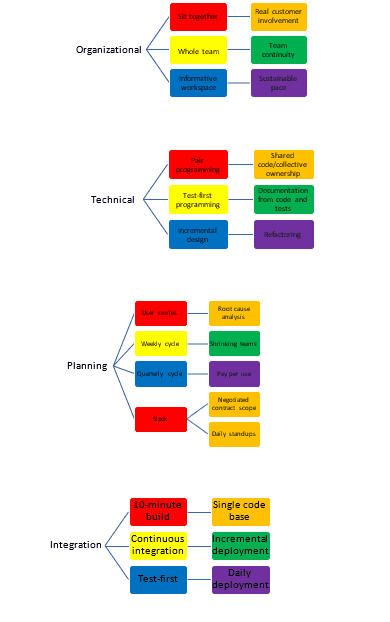
The primary practices must be in place before you implement secondary practices.
For example, with no pair programming, it will be difficult to have a shared code/ownership mindset.
The workspace for Extreme Programming must have visual aids such as flip charts or task boards to communicate status and progress.
You should maintain the workload of the team to avoid burnout. They should not work more than 40 hours per week.
Slack helps in planning to avoid delays because of unlikely events. It is a set of minor activities built into the planning to meet the deadlines.
Small projects have a higher success rate. So, XP recommends incremental delivery. Break down the huge mass into manageable increments of small but regular releases with only the required functionality. Release time is between 2-4 weeks.
Simplicity means designs are as simple as possible. XP doesn’t venture into the complicated end. They keep it as simple as possible and work with small batches.
No wasted motion. Only the important part is coded. Code is only used to suit the current functionality. There are no add-ons, no wasted resources. The XP only modifies to emplace newly added features. Small releases are the emphasis here.
XP decomposes the project into small deliverables. Early small releases provide user feedback and Return On Investment (ROI).
Other practices are:
◉ Continuous Integration: It implies that developers integrate their work daily and do not leave anything out. It is a daily commitment, thus leaving room for early error detection and correction. It helps save accumulated rework.
◉ The real Customer Involvement: This is called onsite customers. This person represents end-users who are expected to provide daily feedback on work done and the next desirable feature.
◉ Pair Programming: In pair programming, the software is built by two programmers sitting side-by-side at the same workstation. This helps code review by a different programmer, resulting in a better product. Pair programming helps knowledge sharing amongst developers as pairs switch. As partners change throughout the day, pair programming can facilitate communication within the team.
◉ Refactoring: This is a quality testing method. It is the reworking of the code for better quality. It is like cleaning the code and it should be a daily routine. You use it to clear the technical debt. You clean up the code without modifying its behavior. Thus improving maintainability. It supports a continuous approach to paying down existing technical debt, though it may slow down current work. It will increase development productivity and save future costs.
◉ Collective Code Ownership: This implies everyone who notices a defect corrects it immediately. It works along with pair programming.
#9. KANBAN
KANBAN is a Japanese term that means signboard. It is about workflow management and ensuring visualization for all. In KANBAN, you hold a card that shows the upstream worker that you are waiting for the work. This is called a pull workstream.
A typical Kanban board is shown below. It is used to manage work.

Sometimes this board is known as an information radiator. This board shows the project status on user stories such as done, ongoing, yet to do.
In Lean manufacturing, the Kanban method is used for scheduling inventory control and replenishment. It is derived from lean principles. The KANBAN methodology is easy to implement.
The basic principles of this methodology are:
Continuous Delivery
You do not start new tasks while you have some work in progress (WIP). However, as soon as WIP completes, you should start the new tasks. There must be a continuous workflow.
In Kanban (like Lean), the aim is to eliminate the WIP and increase productivity. There is no value in WIP nor new activity but in a finished task. You set a limit for the WIP and don’t exceed it.
This continuous and controlled flow prevents the team from being bogged down by overcommitment, which could negatively affect the progress.
Increased Efficiency
Non-value activities are eliminated to focus on business value, thus increasing efficiency.
Reduction of Waste
You can visualize the workflow; hence, waste can easily be removed. With Kanban, organizations stop starting and start finishing.
Lastly, Kanban implements a feedback loop used to improve service delivery. The feedback loop can be reviews or meetings.
One application of the KANBAN method is in manufacturing, where cars are built only on order. Resources are only committed to value. There is no waste.
#10. Lean
Lean is a set of management practices rooted in the Toyota Production System, where they tried to eliminate non-value activities to increase operational efficiency.
The lean concept focuses on value, small batch sizes, elimination of waste, short cycles, frequent reviews, and retrospectives with small improvements.
The seven principles of Lean are:
1. Eliminate Waste: Waste is any activity that does not add value to the finished product. Seven wastes in a software project are extra features, extra processes, partially done work, motion, waiting, task switching, and defects.
2. Build Quality in: Defects should not be allowed, but when this is impossible, try to minimize them. You will do extra work to validate, fix and iterate. Agile does this using Test Driven Developments (TDD), pair programming, and modeling with others (mob modeling).
3. Create Knowledge (Amplify Learning): Team members should be encouraged to reflect and act to improve their approach regularly. Iteration allows team members to learn what exactly the stakeholder wants.
4. Defer Commitment: Keep options open, and use incremental delivery to avoid wasting effort on creating features that were not useful. Software tools for this are emergent designs, automated testing, and patterns thinking.
5. Deliver Quickly: An effective organization gives teams only what they can do so they don’t burn out due to overcommitment. They also allow the team to self-organize, and they deliver quickly.
6. Respect People: Motivate and enable a team to empower and not control them.
7. Optimize the Whole: Look at the bigger picture. Understand how the product synchronizes with the high-level organizational/business objective. The aim is to deliver valuable outcomes to stakeholders.
Source: pmstudycircle.com