Agile is a time-boxed, iterative approach to software delivery that builds software incrementally from the start of the project, instead of trying to deliver it all at once near the end. It works by breaking projects down into little bits of user functionality called user stories, prioritizing them, and then continuously delivering them in short two-week cycles called iterations.
Read More: AgilePM Foundation: APMG International Agile Project Management - Foundation
The Agile methodologies explained below share a large part of the equivalent general way of thinking, just as a considerable lot of similar qualities and practices. From an execution viewpoint, be that as it may, each has its special blend of practices, phrasing, and strategies.
BELOW ARE SEVEN AGILE METHODOLOGIES.
1. Agile Scrum Methodology
2. Lean Software Development
3. Kanban
4. Outrageous Programming (XP)
5. Crystal
6. Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
7. Highlight Driven Development (FDD)
Let’s understand the agile methodologies in detail one by one.
AGILE SCRUM METHODOLOGY
Scrum is an Agile project management framework that can be utilized to oversee iterative and incremental projects, all things considered. Its popularity has increased throughout the years because of its effortlessness, demonstrated efficiency, and capacity to consolidate different overall practices advanced by other Agile models.
Organizations are in any event, hoping to apply Agile Scrum principles to their RPA (Robotic Process Automation) activities to actualize robotization at scale. Embracing Agile Scrum standards gives RPA groups or RPA Centers of Excellence the adaptability to plan and advance business cycles to be mechanized forthright, keep up an effective overabundance of work that advances development, and actualize steady figuring out how proportional start to scale end-to-end automation.
LEAN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
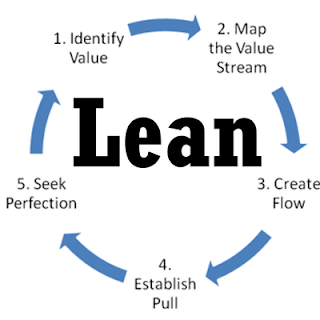
Lean Software Development is an iterative Agile methodology that emphasizes the team on delivering value to the client through effective value stream mapping. It is an exceptionally adaptable, advancing system without unbending guidelines, rules, or strategies.
It gives a dynamic position to people and small teams since this has been demonstrated to be a quicker and more productive technique than a hierarchical flow of control. Lean likewise focuses on the effective utilization of team assets, attempting to guarantee that everybody is as profitable as workable for the most extreme measure of time. It emphatically suggests that automated unit tests be written simultaneously the code is written.
KANBAN
Kanban is an exceptionally visual work process that is the executive’s strategy that is mainstream among Lean groups. Truth be told, 83% of groups rehearsing Lean use Kanban to envision and effectively deal with the making of items with an accentuation on ceaseless conveyance, while not adding more pressure to the software improvement life cycle. Like Scrum, Kanban is a cycle intended to assist groups with cooperating all the more adequately.
KANBAN DEPENDS ON 3 FUNDAMENTAL STANDARDS:
Imagine what you’ll do today (work process mechanization): Seeing all the things inside the setting of one another can be exceptionally enlightening
Breaking point the measure of work in advancement (WIP): This helps balance the stream-based methodology so groups don’t begin and focus on a lot of work without a moment’s delay
Upgrade stream: When something is done, the following most elevated need thing from the accumulation is maneuvered into play
Kanban advances persistent coordinated effort and energizes dynamic, progressing learning and improvement by characterizing the most ideal group work process.
OUTRAGEOUS PROGRAMMING (XP)
Outrageous Programming (XP), initially portrayed by Kent Beck, has arisen as one of the most famous and dubious Agile models. XP is a focused methodology for excellent agile software improvement, zeroed in on speed and constant conveyance. It is expected to improve software quality and responsiveness even with changing client necessities. It advances high client inclusion, quick criticism circles, nonstop testing, ceaseless arranging, and close collaboration to convey working software at exceptionally continuous spans, ordinarily every 1-3 weeks.
The first XP strategy depends on four basic qualities: simplicity, communication, feedback, and courage.
CRYSTAL
Crystal has involved a group of Agile cycle models, including Crystal Clear, Crystal Yellow, Crystal Orange, and others. Each has process qualities driven by a few components, for example, group size, framework criticality, and project needs. This Crystal family tends to acknowledge that each project may require a somewhat customized set of policies, practices, and processes to meet the product‘s unique characteristics.
Presented by Alistair Cockburn, Crystal centers fundamentally around individuals and the association among them while they chip away at an agile software development project. There is likewise an emphasis on business-criticality and business-need of the system under development.
In contrast to traditional development methods, Crystal doesn’t attempt to fix the apparatuses and methods of improvement yet keeps individuals and cycles at the center of the cycle. In any case, it isn’t just individuals or the cycles that are significant, rather the collaboration between them that is most significant.
DYNAMIC SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT METHOD (DSDM)
The Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) is an Agile methodology that outgrew the need to give a typical industry structure to fast software delivery. Since 1994, the DSDM approach has progressed to give a total establishment for arranging, overseeing, executing, and scaling Agile cycle and iterative software development projects.
DSDM depends on eight key rules that immediate the group and make an outlook to convey on schedule and inside the financial plan. These agile standards rotate around business needs/esteem, dynamic client association, engaged groups, regular delivery, integrated testing, and stakeholder collaboration. DSDM explicitly calls out ” fitness for business purpose ” as the essential rules for delivery and acknowledgment of a system, zeroing in on the helpful 80% of the framework that can be sent in 20% of the time.
HIGHLIGHT DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT (FDD)
Highlight Driven Development is a model-driven, short-cycle measure that has worked around software engineering best practices, for example, domain object modeling, developing by feature, and code ownership. The mixing of these practices that brought about a firm entirely is the best quality of FDD.
Source: novelvista.com








0 comments:
Post a Comment