Monday, 3 April 2023
The Top 5 Benefits of Implementing Agile in Enterprise Projects
Monday, 27 February 2023
The Benefits of Agile Methodologies for Software Development
An Overview
Agile Advantages for Software Development
Secure Superior Quality Product
Real-World Examples
Monday, 1 August 2022
Project Management Information System: Features and Advantages
A project is completely based on information and data revolving and communicating with team members. Project management manages all the functions and the data involved in the projects. The way the Project Managers handle projects will vary depending on the project. The PMP certification is a globally perceived project management certification that tests a candidate’s ability to manage a professional project’s people, processes, and business priorities. Further, with the advances in technology, Project Management Information System is developed with the help of software programs and applications.
What is Project Management Information System?
Projects will consist of data from both the internal and external environment. The data from the project is highly valuable and helpful in managing the project effectively. Therefore, the Project Management Information System (PMIS) is a software application used to store, organize, and control project data and information. With the help of the data, project managers can easily execute the deliverables of the project without the need to deliver the real data to the team members. In addition. there are several PMIS available in the market to manage and control the project data. Though there are differences in the various PMIS, the essential features are common. The following are essential features for PMIS.
Need for Project Management Information System
With the old traditional project management systems, project managers have had trouble. It is because of various reasons like managing data and information regarding the project. In addition, project team silos are causing issues like a lack of coordination and collaboration among the teams. The communication and the knowledge between the other teams are also lagging in the traditional project management system. Project Management Information System is developed as a software tool for managing project and resolving the available issues. Moreover, project managers can use it to manage and communicate with the project. It provides various features and benefits when compared to traditional project management.
Essential Features of Project Management Information System
A Project Management Information System requires essential features to deal with its various functions. The following are some of the important features that a PMIS must have:
Planning and Scheduling
It is one of the most important functions of project management. When you initiate a project, the plan and the schedule are the two important components. In addition to that, the PMIS will have scheduling tools with which the project could be under control. Team members will have the schedule to track their day-to-day activities. As a result, the project planning become easier with PMIS. Resource availability, and the costs are linked with the project planning.
Budget and Estimation
Budget and estimation is the feature based on plan and schedule of the project. These estimates are calculated for every project task. Moreover, it helps in calculating the total time for the project completion. In fact, it helps keep track of the current flow and spending for the project. The estimation should consider the resources in the project, time available, and budget from the customer side.
Resource and Procurement Management
Resources of the project may be of several types like human resources, material resources, machinery, etc. The resources are managed on timely basis and updated to avoid wastage of work or idle time. Procurement is also managed with the help of PMIS system. It helps keep track of the costs spent on both the resources and the procurement.
Project Performance
The performance measurement of management is another feature available in the PMIS. The project plan can be changed to obtain the success of the project. The changes has to be useful and must not affect the budget and timeline in higher manner. Hence, calculations like Estimate at Completion (EAC), Estimate to Complete (ETC), Variance at Completion (VAC), etc. will be helpful in managing the projects effectively.
Progress Reporting and Communication
The reports are generated for every task and project to understand the work. The positives and negatives from the project can be studied. Therefore, PMIS system will help generate progress reports to communicate with various team members and stakeholders. In addition, the reports will be analyzed for any requirement. The PMIS is useful for communicating with various project team members.
Integration
The silos in the main issue when dealing with project management. It is because of teams working in different aspects. To overcome the challenges, PMIS is highly helpful in maintaining the data integration in the project. Likewise, the system helps in producing productive and useful information with integration. It also helps in effective management on tasks with timely manner.
Advantages of Project Management Information System
Traditional software project management is harder and tedious to manage the tasks. However, new and advanced Project Management Information System has various advantages over the traditional systems.
Better Collaboration and Teamwork
The teams can collaborate and work together as the communication is effective with the Project Management Information Systems. As a result, team members can work together with better collaboration. Also, the documentation of the project will become easier while working together as a team.
Competitive Advantage
The project teams were migrating to the PMIS-based system to attain its benefits. New and cutting-edge technologies helps in improving the competition in the industry. In addition, customers like their project managers using PMIS system.
Keeping Track of Everything
The main advantage of using the PMIS system is the focus and the track made with it. Project managers can work toward the project’s focus with the various techniques and tools. For example, planning, estimation, management, etc., have helped focus on the project’s aim. With PMIS you can have the complete control of the project. Moreover, cost and time are the two important factors where PMIS provided benefits in projects.
Decision-making Abilities
The decision making is one of the most important roles of the project manager. Nothing will be an issue when a project goes right, and if a project has lost control, the consequences will be serious. In addition, with the PMIS system, project managers can make the decisions on time without facing any serious challenges. For example, any changes or issues in the project will resolve immediately without taking much time.
Manage Multiple Projects at a Time
The number of projects possibly managed with the PMIS system is more. Further, it helps in handling more projects effectively. They are helpful in reducing the errors in the project development.
How to Select Project Management Information System
There are several Project Management Information System available in the market. The following factors will help select the right PMIS for the project.
Suitability
The suitability here refers to the various aspects like the size of the project, team size, cost of the PMIS suite, etc. The compatibility and the other factors are verified before selecting the PMIS for the organization.
Ease of Use
The usability will differ from one PMIS system to another. However, PMIS system should be easier to use without having any challenges in it. Therefore, the team members should not find it difficult to work with it.
Features
The next is the selection of the features that are available in it. Mostly all the PMIS systems will have the basic essential features for managing the project. Moreover, the required features should be verified and selected for best results.
Mobile Application
Mobile application availability should be verified before buying the Project Management Information System. The mobile application helps users to manage the task effectively without the need for a computer.
Communication
The platform or option for communication and sharing the files is verified while working on selecting the PMIS system. Here, it is important to communicate with the team members in the project.
Third-party Application Integration
PMIS system should have capability of integrating third-party applications in it. In addition, it will help manage the tasks with integration and collaboration with the other tasks.
Examples of Project Management Information System
There are several Project Management Information Systems available in the market. Budget and feature requirement are the two basic factors while selecting the PMIS. The following are some examples of PMIS systems available.
◉ ProofHub
◉ Basecamp
◉ Citrix Podio
◉ Jira
◉ Trello
Apart from these, there is numerous other PMIS software that is available. The software tool selection is solely based on requirements, budgets, and ease of use.
Source: invensislearning.com
Wednesday, 13 July 2022
How to Incorporate Change Management into Agile Projects
Change management is the most important advantage when dealing with agile project development. With that, you can easily accept and implement the changes in the project. Several factors are available that are important to deal with while implementing the changes. The changes are mainly in the design, development, and testing of the project. The acceptance of the changes in the project is based on several factors. The reasons for the changes in the software are the less planning and the customer requirements. In traditional software development, changes are not possible as they are based on sequential phases, and once a phase is completed, it cannot be developed again. Hence, the software development with the agile model will produce various benefits in achieving customer satisfaction and productivity.
Read More: PMI Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)
Software development is not based on a single essential output. Instead, the customer comes up with some changes in the features and functionalities in the middle of the project. Developers and Testers can suggest some changes while working on the development. In such conditions, Agile-based software development helps incorporate the identified changes effectively. So, with effective change management implementation with agile, all the stakeholders involved in the project are satisfied. In addition, Change Management Certification Training is one of the growing certification courses that is apt for professionals looking forward to gaining a comprehensive understanding of how the process of organizational change or transformation occurs, and how one can ensure it is done in a structured/ organized fashion.
This blog will mainly focus on discussing change management implementation in software projects. However, before all that, let us understand what change management is.
What is Agile Change Management?
The method of agile change management is the term that enhances to take over the momentum around the globe. There are possibilities of several changes in the intermediate level of the project. The changes from the customer side or other stakeholders take some time to review and initiate. First, the team will check the need for the change in the project and then the possibilities of accepting the change. Agile is a highly helpful approach when coming to change management. Moreover, Agile change management helps focus on the changes from any stakeholders and of any size, from minor to major.
Many organizations will not ask for the customer requirements completely in advance, causing the changes in the middle. The changes will cause trouble for the developing team. Therefore, it is important to note the required changes and discuss them among the team members. In the case of change management, several phases are involved, which are planned accordingly. Hence, this was the reason for adopting agile projects for the change management and considering each phase like development, designing, and testing the cycles over the change management.
On the other hand, every project management elaborates on progressing things in technical ways to reach the particular things through the quality, cost, and constraints. The popularity of agile increases the iterative segments broken through some tackles. The agile project will have to keep the change management to support the adoption and usage necessary for accurate results achievement. And therefore, the importance of change management over agile was much needed throughout the project lifecycle.
Now, let us discuss the various ways in which change management is incorporated into agile projects.
Ways for Incorporating Change Management Into Agile
It is simple when we talk theoretically about change management, but implementing the changes in the software project is highly difficult. It is to understand that Agile assists in accepting, implementing, and managing the required changes in the project. In addition, change management is the success of the agile approach, and it has to be effectively handled to avoid issues and failures in the project. Following are the ways to incorporate change management into agile projects.
Accept the Change and Make Adjustments
Small or even minor changes in traditional software development projects are hard to implement. But in the Agile software development model, the changes help in reducing the number of errors and failures. An excellent way to implement the change is to verify it and accept it based on the various acceptance criteria. Then, based on the available iterations, the changes are planned and initiated. The base idea here is to accept the changes requested by both stakeholders and the customers. The acceptance is based on the software development feasibility that should not affect the project’s schedule and budget constraints.
Design for Customer Requirements
Change implementation helps in meeting the customer requirements in software development. Customer satisfaction is possible with proper change implementation in the projects. Every phase of the development requires better communication with the customer. The acceptance and declination of the changes are vitally discussed. Once the changes do not meet customer expectations, the performed changes are not successful. Thus, connecting and communicating with the customer is most important while implementing the changes in the software development process.
Focus on User Stories and Change Vision
The user stories are the most valued activity, and it is vital to design and develop from the iteration. The most recent and important stories are delivered to all the project developers and testers to verify any required changes. The user stories developed at the project initiation may change when the customer needs some additional requirements. Therefore, it is important to identify the changes at the development stage itself. The prioritization of the user stories will help manage the changes from the acceptance stage. It will help manage the changes and avoid delays while working on the changes. The vision for the change is important, and hence the vision should be kept in focus.
Provide Power to People Working on Change
When a change is implemented in a project, several people will be working towards it. The people working on the change must have the power to make the decisions in their tasks. Providing powers to the people will help to complete the tasks on time without any delay as they do not require to wait for the higher authorities to deal with it. They will drive the change from the beginning to avoid additional and major changes in the intermediate stages. The customer is the first point for change requirements, and hence the discussion with the customer is important. Developers need to communicate with the customers at regular time intervals to understand their needs. In addition, they are responsible for delivering the project successfully and achieving customer satisfaction. It also helps the project team’s expertise in change management and the associated principles, which will be helpful in future projects.
Update User Stories to Make Them Accurate
The acceptance criteria and descriptions of the project are kept accurate and up to to date. The user story is the feature description to discuss the functional abilities that it can do. In agile, every feature doesn’t relate to one another, and hence the user stories are separate. Any changes or modifications by the customer or the product owner are the prime cause of change management. Dissatisfaction from the customer side is highly possible if the changes are not effective as per the plan. Therefore, updating user stories and descriptions is essential at frequent time intervals. The accuracy here refers to the feedback from the customer side on the acceptance and any changes made from their side. Therefore, the need for accuracy in user stories is important.
Improve the Employee Communication
Communication is the top priority when dealing with change management in agile project management. When dealing with the changes in the project communication, it plays a vital role. The developers, testers, product owners, and the other internal stakeholders are essential to communicate themselves a regular time intervals. It helps them figure out the possibility of the changes and acceptance criteria. The possible options to incorporate the change are important while dealing with change management. Hence, communication on the change plan, design, and development are essential among the team members.
Increase the Team Collaboration
The collaboration between the developing and testing teams is significant. The team collaboration help understand how the changes are according to customer requirements. If any errors or quality issues occur due to the change implementation, the tester can immediately revert to the developing team to resolve it immediately. Change discussion or change meetings are necessary during the development or change implementation to maintain and manage the changes in the project. The tests become more effective when the teams collaborate, and hence the quality of the final product will be more. The team leaders are responsible for conducting these change meetings and discussions among the team to increase the collaboration among the teams.
Prioritize and Handle Changes Effectively
The identified, accepted, and implemented changes are made based on priority. The priority is required to deal with the right change at the right time. It is important to note the challenges arising while working on these changes. As part of the change implementation in the projects, a team will be helpful. The change team is a team focusing only on the successful completion of the changes in the project. The review of the change proposal is essential for dealing with the changes in acceptance of refusal. Therefore, the change decisions are important as they help make the right decisions to implement the change in projects. In addition, the development and testing teams need to work together to make the change management effective. Priority in the change implementation is also important as this helps in working based on the significance.
Manage the Change and Sprints
The sprints managed in the project should not disturb in the middle as this can cause serious issues leading to sprint failure, which causes delays. The changes are implemented at the initiation of the future sprints of the project. Every team member needs to know the change, and hence change requests and status are publicly visible. The discussion on the change before the sprint will help obtain feedback and suggestions on the acceptance or rejection of the change. The yes or no answers from the team members are based on change review, time, and the budget available in the project. The application release and project schedule is important during change management. The surprise changes will cause frustration and impact the product development quality.
Communicate and Manage Customer Requirements
Communication between the managers and customers is important in project development. The team members should make the better communication among themselves and other teams to make the effective collaboration. Therefore, some communication methods like team meetings, video conferencing, audio conferencing, etc., help deliver the insignificant changes form. In addition, team collaboration is possible with the increase in communication between the team members. Therefore, team members are vital in providing the changes in the project. There are different methods of communication, and the customers can prefer anyone to interact with the project managers to achieve the best results.
Hope you have got an idea about implementing the changes in project management. Now, let us study the benefits of agile change management.
Benefits of Change Management
◉ Achievement in change management provides a variety of benefits. It helps to support the effective transition from the old progress to the new one and results in effective results for the organization in adopting the change management
◉ Change management encompasses different approaches toward result production during meticulously planning and managing systems
◉ Data and resource requirements for the project are possible with change management
◉ It extends to modifying the resources through the business to support the changes
◉ Change management helps in the easier addition of changes with reduced cost
◉ It encompasses an effective strategy for mitigating the complicated issues raised during the development
◉ Helps to reduce the failure possibilities in solution achievement
◉ It enables the daily routine to run the business with effective changes
◉ Change management improves the communication between the team members and other teams in the organization. Hence, communication seems to be the key element of the organization’s development
◉ Project development helps to modify the strategies for the extensions of best results
◉ It enables access to the competitive edges for positive organizational modification and helps follow the consistency over the success points
◉ It clears the business through effective consistency and clarity of the data and sets the best framework for the best business direction
◉ Progressing data within the fixed budget is much required. The improvement in the efficiency of the teams is another advantage
Overall, change management helps the entire business and projects with many benefits and enables recent technologies to develop works. Moreover, the changes are now feasible with the frameworks with advanced features and functionalities.
Source: invensislearning.com
Monday, 23 May 2022
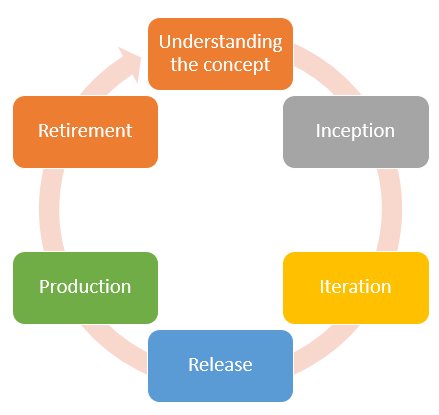
What is Agile Methodology? A Comprehensive Guide on Agile Methodology
What is Agile Methodology?
Agile Model vs. Waterfall Model
Benefits of Agile Methodology
Phases of Agile Methodology
Key Agile Methodologies
Best Practices of Agile Methodology
Tuesday, 2 November 2021
Self Organizing Teams in Agile: Why Is It The New Big Thing?
At your workplace, you probably are working under some manager who assigns you tasks on a regular basis, you have
Self-organizing groups are at the core of the Agile approach however constructing one has never been a simple errand. Wikipedia characterizes self-association as “The process where a structure or pattern appears in a system without a central authority or external element imposing it through planning”. More difficult than one might expect without a doubt.
We as a whole realize that giving a group the authority of turning out to be self-composed is a ton unique in relation to the customary working technique for delegating assignments where the vast majority are utilized to. It requires some investment for progress from a customary group model to a self-organized one—and this cycle, as a rule, doesn't get refined in one meeting yet requires steady correspondence and preparation of colleagues which encourages this change cycle. Nonetheless, this hierarchical change is totally worth the underlying venture and it will pay off toward the end. The outcome will be shockingly great products made by happy employees. As you most likely are aware, everyone needs to see this.
How self-organization enhances our agility and what are its benefits?
1. Higher speed
Self-organizing teams quickly decide how to meet certain deadlines in the product development roadmap. This feature is extremely important especially for startups where the company faces loads of change requests from customers. Self-organizing teams ensure a higher development velocity that enables the company to respond to market fluctuations more rapidly and turn around a product much faster.
2. Extreme agility
It's entirely expected to see significant priority changes in Agile particularly before the start of the impending Sprint (Product Owner, as a rule, does this). Self-organized groups have a bit of leeway compared to traditional groups as they can rapidly change gears and push ahead without hanging tight for somebody's authorization. This will permit improvement groups to focus on basic undertakings that have higher-worth and a more prominent rate of profitability.
3. Increased quality/customer focus
Rather than simply doing what the manager says, self-organized groups will in general zero in on what the client truly needs or potentially needs. They pay attention to client criticism and feel amazingly dependable of building an item that coordinates these highlights and measurements. A self-arranging group focuses on building an item that will fulfill the purchaser’s/clients' needs.
4. Less need for team management
Checking worker statuses, allocating tasks, figuring cost of assets, occupying time sheets… All sounds insane old to me. On the off chance that you are determined to build Agile groups, you should feel the equivalent. A self-composed group is exclusively mindful of appointing and following its work and announcing its own personal advancement.
5. True teams vs hidden managers
You may have found out about the "hidden manager" hypothesis. This straightforward principle demonstrates that the lion's share of customarily oversaw groups can really have a doled out (not formally) colleague as a group level administrator. This individual is generally called the "go-to fellow". Contingent upon another person's assertion is totally against oneself sorted out group hypothesis as self-composed groups see each other's jobs and assignments undeniably more and depend far less on one's expertise or position in the group.
6. Increased employee satisfaction
Self-organizing team members have higher worker fulfillment. Toward the day's end, we go through a large portion of our day at the workplace and it bodes well to see more joyful representatives by decreasing the miniature administration model, for example, indiscriminately following requests or holding up director's endorsement prior to pushing ahead. Getting the entire team to contribute and pushing the task ahead are keys for bliss at work.
A few associations endeavor to make self-organizing groups and find that the group isn't considered responsible, or the management is as yet instructing everybody. It is difficult to change individuals' perspectives particularly in the event that they have been doing it for a long time. You simply need to keep calibrating your cycles and it will get simpler to find that balance over time. It likewise requires the correct organization culture and workers who are prepared to acknowledge another group model which urges colleagues to take responsibility for and measures.In his book “Agile Project Management with Scrum”, Ken Schwaber described how it is our instinct to expect others to make decisions that we should be making ourselves:
“Being managed by someone else is totally ingrained in our life and work experience. Parents, teachers, and bosses who teach us to self-manage instead of striving to fulfill their expectations are rare. Why should we expect that when we tell a Team that it is responsible for managing itself, it will know what we are talking about? “Self-management” is just a phrase to them; it isn’t yet something real. A Team requires concrete experience with Scrum before it can truly understand how to manage itself and how to take the responsibility and authority for planning and conducting its own activities. Not only must the ScrumMaster help the Team to acquire this experience, but the Scrum Master must also do so while overcoming his or her own tendencies to manage the Team. Both the ScrumMaster and the Team have to learn anew how to approach the issue of management.”
The 3 Attributes of Self-Organizing Teams
◉ A self-organizing group is where colleagues will choose themselves who does what; the group will deal with issues and have some capacity to eliminate their own personal blockages. Obviously, there are groups who are more self-sorting out than others and groups which have more authority than others.
◉ In a self-organizing group, there is no dynamic everyday management of the group. The group is successfully left to deal with their own personal work. To my psyche, this is a more grounded type of self-sorting out.
◉ A self-coordinated group is a group that defines its own personal objectives, chooses its own personal targets, and decides its own personal needs.
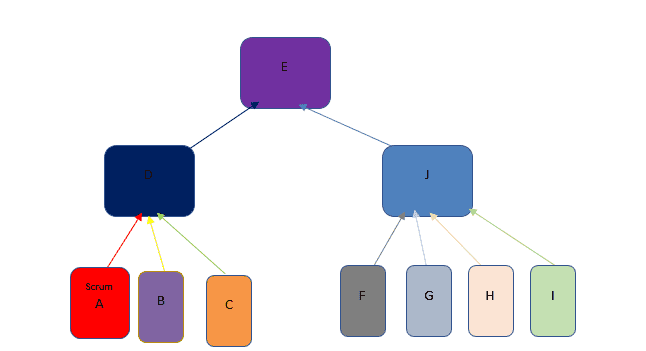
Self-organizing teams in Scrum
Scrum is as yet the most well-known Agile system in the software development field. Consequently, it's critical to obviously comprehend Scrum jobs and how to incorporate these parts with a self-arranging group model all through the development lifecycle.
◉ In the self-organizing group model, nobody (not even the Scrum Master) advises the Development Team on how to transform Product Backlog into Increments of possibly releasable usefulness.
◉ The Scrum Master is the servant leader and serves the Development Team in a few different ways, including Coaching the Development Team in self-association and cross-usefulness
◉ Before the finish of the Sprint Planning, the Development Team ought to have the option to disclose to the Product Owner and Scrum Master how it means to fill in as a self-organized group to achieve the Sprint Goal (submitted client stories) and make the foreseen Increment.
Source: novelvista.com
Monday, 5 July 2021
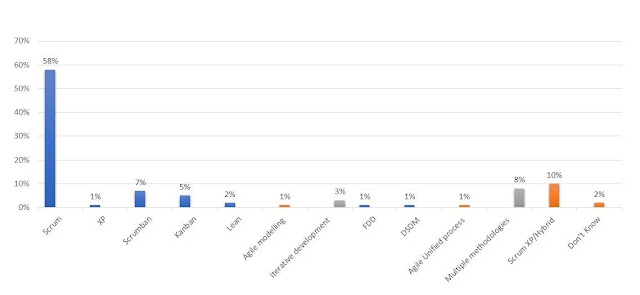
10 Popular Project Management Methodologies
Project management methodologies have essential roles in how you govern your project. Until a few years back we used to have one popular project management methodology, which is the traditional project management methodology or waterfall.
This methodology was useful for construction types of projects where you have a well-defined scope; however, IT projects had trouble with this project management approach because these projects had continuous changes and the waterfall method was not suited for projects with changing requirements.
So project managers needed new methodologies to help deal with changing requirements. Consequently, Agile methodologies came, and afterward, many more new more project management approaches followed.
In today’s post, I will introduce you to ten popular project management methodologies.
Project Management Methodologies
A project management methodology is a set of guidelines and best practices that help you to complete your project efficiently with less obstruction.
Every project is unique and you need the right methodology for your project.
The project management framework evolved from a traditional approach to Agile, resulting in significant changes in the way we carry out the project activities.
Project management approaches affect the culture of the organization and the project team. You need to understand the culture to work seamlessly with your team.
Here are the top ten project management methodologies used by organizations to complete their projects:
1. Waterfall
2. Scrum
3. Disciplined Agile
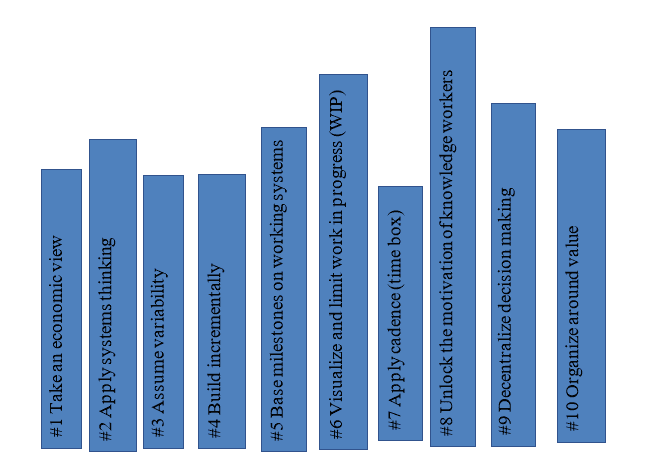
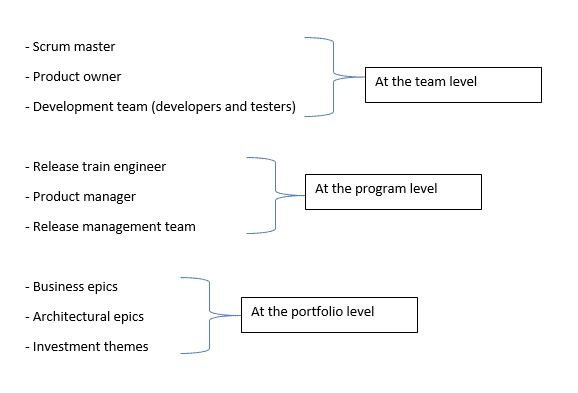
4. SaFE (Scaled Agile Frameworks)
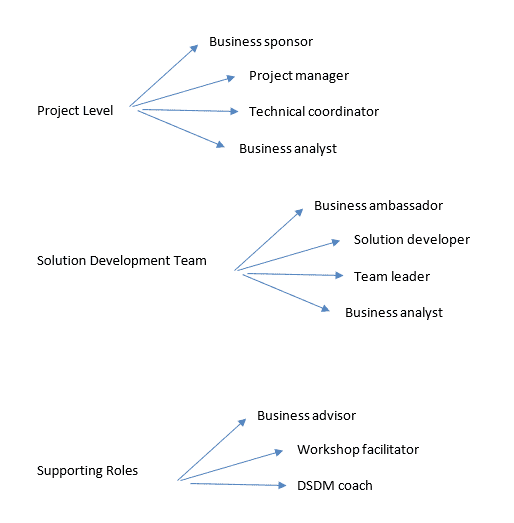
5. DSDM (Dynamic Systems Dev. Method)
6. LeSS (Large Scale Scrum)
7. Scrum of Scrum (SoS)
8. XP (eXtreme Programming)
9. Kanban
10. Lean
#1. Waterfall
This is the most popular project management methodology. Here you have a well-defined scope and activities are planned in sequence. You invest a lot of effort into collecting requirements and then developing the project management plan. Once all plans are developed, baselines are created, you get them approved and follow them religiously.
Changes in the project management plan or baseline are not easy. All change requests go through a lengthy process to get approved. After the approval, you will update your plans and baselines.
Changing requirements in this project management approach are difficult and costly. All change requests go through a time-consuming change management process.