Monday, 27 February 2023
The Benefits of Agile Methodologies for Software Development
Friday, 24 February 2023
The Role of Agile in Digital Transformation
Definition of Agile Methodology
What is Digital Transformation?
The Intersection of Agile and Digital Transformation
The Benefits of Using Agile in Digital Transformation
Implementing Agile in Digital Transformation
Overcoming Challenges and Obstacles in Agile Digital Transformation
Thursday, 23 February 2023
ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification OGA-031: Ace It with Practice Tests
Passing the Open Group OGA-031 exam requires much effort and functional study materials like practice tests. Discover the preparation tips and explore some of the career opportunities of earning The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation certification.
The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification is valuable for enterprise architects, IT architects, and other professionals who work with enterprise architecture. This certification demonstrates that the holder understands the ArchiMate modeling language and its application in enterprise architecture.
To obtain the OGA-031 certification, candidates must pass a certification exam that covers particular topics. A few of them are as follows-
- Generic Metamodel
- Language Structure
- Strategy Elements
- Motivation Elements
- Language Customization Mechanisms
- Business Layer
What Is Open Group ArchiMate?
The Open Group ArchiMate is a modeling language used to describe, analyze, and visualize architecture within an enterprise. With the release of version 3.1 of the ArchiMate specification, The Open Group has introduced several new features and improvements.
Organizations worldwide recognize the Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification as a standard of excellence in enterprise architecture. It provides a common language and framework for communicating architecture concepts and enables organizations to align their business and IT strategies.
Preparation Tips to Ace the Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification:
Preparing for The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification can be challenging, but with the right resources and study plan, you can increase your chances of passing the exam. Here are some tips to help you prepare for the certification exam:
Familiarize Yourself with the ArchiMate 3 Specification:
The certification exam is based on the ArchiMate 3 Specification, so it's essential to understand the concepts, language syntax, and modeling principles described in the specification. The Open Group offers free online resources to help you get started.
Attend Training Courses:
The Open Group offers in-depth training courses that cover the ArchiMate 3 Specification and can help you understand the key concepts and principles. You can also attend courses offered by accredited training providers.
Also Read:
Practice with ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification Sample Questions:
The Open Group offers sample questions that can help you familiarize yourself with the questions that may appear on the certification exam. Studying with sample questions can also help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge.
Use Different Study Materials:
Several study materials, such as study guides, practice exams, and flashcards, can help you prepare for the certification exam. You can also join online communities and discussion forums to get tips from other candidates who have taken the exam.
Take OGA-031 Practice Exams:
Practice exams can help you assess your knowledge and identify areas where you need to focus your study efforts. The Open Group offers practice exams that simulate the actual certification exam. Rigorous practice on the OGA-031 practice tests could familiarize you with the exam structure, which helps in attempting a maximum number of questions.
Stay Up-to-Date with the Latest Developments:
The Open Group regularly updates the ArchiMate 3 Specification, so staying current with the latest developments is important. You can subscribe to The Open Group's newsletter to stay informed.
What Possible Career Benefits Can You Have with the OGA-031 Certification?
Enhanced Career Opportunities:
The Open Group OGA-031 certification can increase job opportunities and career prospects. Organizations around the world recognize this certification as a standard of excellence in enterprise architecture and look for certified professionals to fill enterprise architecture positions.
Higher Salary Potential:
According to PayScale, professionals with enterprise architecture skills earn an average salary of $120,000 per year. Obtaining The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification can increase your earning potential and negotiate higher salaries.
Better Job Performance:
The ArchiMate modeling language provides a common language and framework for communicating architecture concepts and strategies. By obtaining The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification, you can improve your ability to communicate with stakeholders and align business strategies with IT strategies, leading to better job performance.
Increased Industry Recognition with the Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification:
The OGA-031 certification is recognized by industry leaders and organizations worldwide as a standard of excellence in enterprise architecture. Being a certified professional can enhance your reputation and credibility in the industry.
Career Advancement with the ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification:
The Open Group OGA-031 certification can open doors to career advancement opportunities. With a comprehensive understanding of ArchiMate and its application, you can take on more senior-level roles in enterprise architecture and lead architecture projects.
Bottom Line:
In conclusion, The Open Group ArchiMate 3 Foundation Certification is a valuable credential for professionals working in enterprise architecture. It demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of ArchiMate and its application and provides a common language and framework for communicating architecture concepts and strategies.
Wednesday, 22 February 2023
The Use of Agile in Large-scale Enterprise Projects
Definition of Agile
Overview of Agile in Enterprise Projects
Advantages of Agile in Large-scale Projects
Implementing Agile in Enterprise Projects
- Assessing current project management processes: This step involves analyzing the current project management approach and identifying any areas that may need to be changed or improved to integrate Agile principles successfully
- Choosing the right Agile methodology: This step involves researching different Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean, and determining which will best fit the organization’s specific needs and goals
- Building an Agile team: This step involves assembling a team of individuals with the necessary skills and mindset to work in an Agile environment. This includes selecting team members who can work collaboratively, think creatively, and adapt to change
- Establishing an Agile culture: This step involves creating a work environment that supports and encourages Agile principles and practices throughout the organization. This includes promoting transparency, communication, and continuous improvement
- Training and education: This step involves providing training and education to all team members on the chosen Agile methodology and how to work in an Agile environment. This helps the team members to understand the benefits, principles, and practices of Agile methodologies
- Implementing Agile practices: This step involves incorporating Agile practices, such as sprints, stand-up meetings, and retrospectives, into the project management process. This helps to ensure that the team is working in an Agile manner and that the project is on track to meet its goals.
- Continuously monitoring and improving: This step involves monitoring the progress of the project and the effectiveness of the Agile implementation and making adjustments as needed to ensure that the project is successful
- Reviewing and reporting: This step involves regularly reviewing the project’s progress and providing reports to stakeholders on the progress, deliverables, and any issues encountered
Challenges of Agile in Enterprise Projects
- Resistance to change: Agile requires a significant shift in mindset and practices, and some team members may be resistant to change, particularly those who are accustomed to traditional, more structured project management methods
- Lack of clear requirements: Agile emphasizes flexibility and adaptability, making it difficult to define clear requirements upfront. This can lead to scope creep and delays in project completion
- Difficulty in coordinating multiple teams: In an enterprise setting, multiple teams may work on different parts of the same project, making coordination and communication more difficult. This can lead to conflicting priorities and delays in project completion.
- Limited visibility into progress: Agile methods can make it harder to track progress, as the focus is on delivering working software incrementally rather than on specific deliverables. This can make it difficult for stakeholders to assess progress and make decisions
- Difficulty in measuring success: Agile methods can make it harder to measure success in terms of traditional metrics such as cost and schedule. This can make it difficult for stakeholders to assess the value of the project and make funding decisions
- Scaling Agile: Scaling Agile methodologies and practices to large enterprise projects can be a significant challenge. Agile methodologies are often best suited for small, cross-functional teams and may be less effective when applied to large, complex projects with multiple teams and stakeholders
- Lack of governance and oversight: Agile methodologies place a lot of autonomy and ownership on individual teams, but this can also lead to a lack of governance and oversight, which can be a problem in large organizations. This can lead to confusion, delays, and a lack of accountability
Successful Agile Case Studies in Enterprise Projects
Monday, 20 February 2023
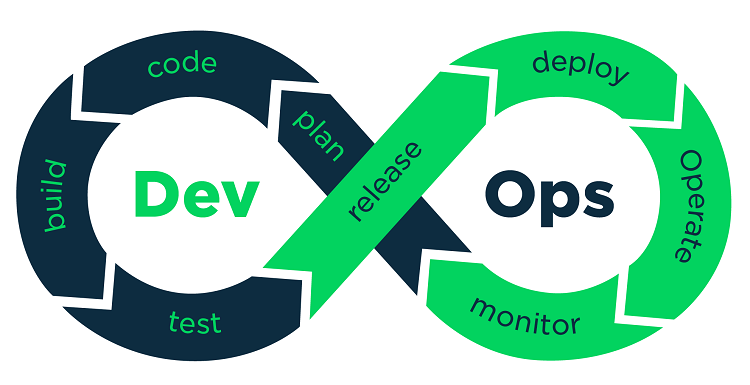
5 Ways to Improve Your DevOps Workflow
What is a Typical DevOps Workflow?
How to Improve Your DevOps Workflow?
Creating a Culture of Collaboration and Communication
Utilizing Agile Methodologies
Using Version Control Systems
Implementing Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
Wednesday, 15 February 2023
Implementing a Project Management System: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is a Project Management System?
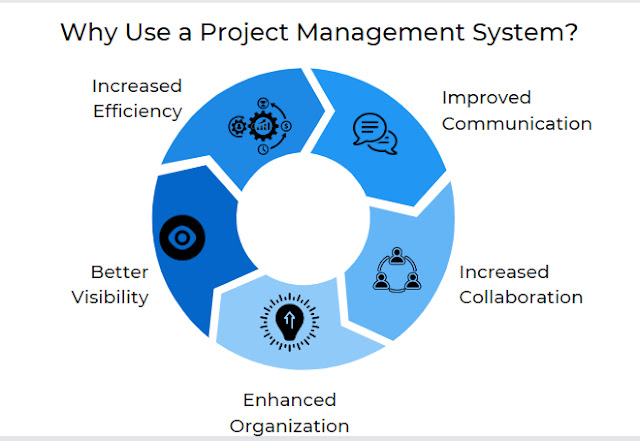
Why Use a Project Management System?
How to Implement Project Management System?
Monday, 13 February 2023
Unleashing the Power of a Project Management Office: Maximize Benefits for Your Business
Introduction
Improved Project Management
Increased Visibility and Control
Better Resource Allocation
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Standardized Processes and Procedures
Friday, 10 February 2023
How can Six Sigma Improve Employee Engagement?
Understanding Employee Engagement
The Relationship Between Six Sigma and Employee Engagement
How can the DMAIC Process be Applied to Improve Employee Engagement?
| DMAIC Step | Description |
| Define | The problem or opportunity related to employee engagement you want to improve. For example, you can improve job satisfaction or reduce turnover rates. |
| Measure | Collect data on employee engagement using surveys, interviews, or other metrics. This data will be used to determine the current engagement level and track progress over time. |
| Analyze | Use statistical tools to analyze the data collected in the measure phase. Identify trends, correlations, and root causes of low engagement levels. |
| Improve | Develop, and implement solutions to address the root causes of low engagement. This could include changes to work processes, improvements to the work environment, or new employee engagement programs. |
| Control | Monitor and evaluate the results of the improvement efforts and make ongoing improvements as needed. This will ensure that employee engagement remains high over time. |
And here’s a sample table that summarizes the data collected and analyzed in the Measure and Analyze steps of the DMAIC process:
| Data Category | Data Point | Data Collection Method |
| Job Satisfaction | Percentage of employees who rate their job as satisfying | Employee Survey |
| Work-Life Balance | Percentage of employees who feel that their work and personal life are balanced | Employee Survey |
| Job Stress | Percentage of employees who feel that their job is stressful | Employee Survey |
| Turnover Rates | Percentage of employees who have left the company in the past year | Human Resources Data |
Examples of Organizations Successfully Using Six Sigma to Improve Employee Engagement
Wednesday, 8 February 2023
Using Six Sigma to Improve Safety in the Workplace
Workplace safety is a top priority for any organization, as a safe environment protects employees, helps maintain a positive work culture, and improves overall productivity. To achieve this, companies often adopt various methods and techniques, and Six Sigma is one such approach that has proven to be highly effective in improving safety in the workplace.
In this blog, we will explore how Six Sigma can be used to improve safety in the workplace. By the end of this blog, you will understand the benefits of using Six Sigma to improve safety in the workplace and how to implement it effectively.
How Can Six Sigma Improve Your Safety Performance?
Six Sigma is a quality management method focusing on continuous improvement and minimizing defects. It has been used in various industries to improve processes, reduce costs and increase customer satisfaction. Recently, Six Sigma has been applied to workplace safety with great success, providing a structured and data-driven approach to identifying and eliminating root causes of safety issues.
Safety Risk Assessment
One of the first steps in using Six Sigma to improve safety in the workplace is to conduct a safety risk assessment. This involves identifying potential workplace hazards and assessing each hazard’s likelihood and consequences. This information is then used to prioritize areas for improvement, with the most significant risks being addressed first.
DMAIC
The Six Sigma methodology is based on the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) process, which helps to identify and eliminate the root causes of problems. During the Measure phase, data on the frequency and severity of safety incidents is collected. This data is then analyzed to determine any patterns or trends that could indicate a root cause of the safety issues.
In the Analyze phase, root cause analysis is performed to identify the underlying reasons for the safety incidents. This may involve reviewing procedures, interviewing employees, and conducting site inspections. Once the root causes have been identified, the Improve phase can begin.
Tools and Techniques
There are a variety of tools and techniques that can be used to improve safety in the workplace, including process improvements, workstation design, and employee training. For example, changing procedures to eliminate hazardous steps, improving lighting and ventilation, and providing regular safety training for employees can significantly reduce the number of safety incidents.
Implementing Six Sigma for safety requires a commitment from all levels of the organization. This includes training programs for employees, as well as a cultural shift towards a safety-first mentality. In addition, involving employees in the process is important, as they often have valuable insights and can be a key source of improvement ideas.
Finally, it is important to measure the success of a Six Sigma safety initiative. This can be done by tracking the number of safety incidents and monitoring improvements over time. Sustaining these improvements requires continuous monitoring and improvement efforts.
In conclusion, using Six Sigma to improve safety in the workplace can be a highly effective approach. By utilizing a structured and data-driven methodology, companies can identify and eliminate root causes of safety issues, resulting in a safer work environment for employees and improved productivity for the organization.
Using the DMAIC Model for Workplace Safety
DMAIC is a problem-solving methodology used in Six Sigma, a data-driven approach to process improvement. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. When applied to workplace safety, the DMAIC model can help organizations identify and address safety issues, improve safety processes, and establish a system for ongoing monitoring and improvement.
The five phases of DMAIC are:
◉ Define the problem or opportunity related to workplace safety
◉ Measure the current performance and identify key metrics
◉ Analyze the root causes of safety issues
◉ Improve processes to eliminate or reduce the risk of accidents
◉ Control the changes to ensure ongoing improvement and prevent recurrence of the problem
The Define Phase
The Define phase in Six Sigma is the first step in the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) process and is focused on clearly defining the problem and the project goals. In terms of improving safety in the workplace, the Define phase can play a crucial role by helping organizations:
Identify the root cause of safety issues: By clearly defining the problem and its scope, organizations can better understand the underlying causes of workplace accidents and injuries, which can help them to implement targeted and effective solutions.
Set clear goals and objectives: The Define phase allows organizations to establish specific and measurable goals for improving workplace safety, which can help to prioritize and focus their efforts.
Engage stakeholders: The Define phase is also an opportunity to involve relevant stakeholders, such as employees, managers, and safety experts, in improving safety. This can help ensure that everyone is aligned and invested in the project’s success.
Allocate resources: By clearly defining the problem and the goals for improving safety, organizations can better allocate resources, such as time, money, and personnel, to support their efforts.
Overall, the Define phase in Six Sigma can play a critical role in improving safety in the workplace by helping organizations to establish a clear understanding of the problem, set realistic and measurable goals, engage relevant stakeholders, and allocate resources effectively.
The Measure Phase
Six Sigma’s “Measure” phase is designed to gather and analyze data related to a particular problem or issue. In the context of workplace safety, this phase can help identify and quantify potential hazards, risks, and incidents that negatively impact the health and well-being of employees. The data collected in this phase can then be used to establish a baseline of the current situation, which is necessary for measuring progress and making data-driven decisions.
Using statistical tools and techniques, the measure phase can help identify the root cause of safety problems, measure the severity of each issue, and prioritize actions based on the potential impact of each hazard. The data gathered during this phase can also be used to track improvements over time, validate the effectiveness of safety interventions, and evaluate the overall effectiveness of the safety program. Overall, the measure phase in Six Sigma can provide valuable insights into the current state of workplace safety and help organizations to continuously improve and make their workplace safer for employees.
The Analyze Phase
The “Analyze” phase in Six Sigma is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problems and defects that contribute to safety hazards in the workplace. During this phase, data is collected and analyzed to determine the causes of the safety issues. This information is then used to determine the most appropriate solution for the problem. As a result, organizations can create a structured and systematic approach to safety improvement using the Six Sigma methodology.
The data-driven analysis in the Analyze phase helps identify the critical factors contributing to workplace accidents and incidents and provides the foundation for effective corrective and preventative action. The outcome of the Analyze phase is a clear understanding of the causes of the safety issues and a roadmap for improvement.
The Improve Phase
The “Improve” phase of the Six Sigma methodology can help improve workplace safety by using data-driven decision-making and problem-solving techniques to identify, evaluate and implement solutions to improve safety performance. This phase involves the following steps:
Generate and evaluate alternative solutions: In this step, various alternative solutions to improve safety are generated and evaluated to determine the most effective and feasible.
Choose a solution and develop an implementation plan: Based on evaluating alternatives, the best solution is chosen, and an implementation plan is developed to implement the solution.
Implement the solution: The implementation plan is executed, and the solution is implemented to improve workplace safety.
Monitor and sustain the improvement: After the solution is implemented, it is important to monitor the results to ensure that the improvement is sustained and to identify any new risks or issues that may arise.
By following these steps, Six Sigma’s “Improve” phase can help organizations improve their safety performance and reduce the risk of workplace accidents, incidents, and injuries.
The Control Phase
The “Control” phase in the Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology is aimed at ensuring the improvements made in the “Improve” phase are sustained over the long term. This is accomplished by establishing procedures and processes that monitor and control the new practices and processes implemented in the “Improve” phase.
In the context of improving safety in the workplace, the “Control” phase can help to ensure that the changes made to improve safety are consistently implemented and maintained. This can be accomplished by establishing safety protocols, developing monitoring and reporting systems, and providing training and support to employees. The “Control” phase also helps to ensure that the improvements made to safety are continuously reviewed and updated as necessary to ensure that the workplace remains safe for employees over the long term.
Source: invensislearning.com