Friday, 30 December 2022
What is the difference between PMOs and Project Managers
Thursday, 29 December 2022
Understanding of PRINCE2 Methods and Certifications
Working within a framework is critical when it comes to project management. So, PRINCE2 managers and team members need clear roles and responsibilities and measurable goals, processes, and best practices. In addition, this helps managers prevent avoidable delays and expenses by keeping the project lifecycle as efficient and aligned as feasible.
PRINCE2 is a methodology that works for various projects, industries, tools, and teams. This project management technique can be rigidly applied or combined, with a hybrid project management methodology combining two or more methodologies to respond to the particular elements of a project environment.
It is critical to acquire the appropriate credentials and certification if you work in a project management methodology sector. PRINCE2 is one of just a few core certifications available. PRINCE2 Practitioner Certification is one of the renowned Project Management certification programs that are apt for professionals looking forward to gaining a comprehensive understanding of the PRINCE2 methodology, which is a process-based approach that focuses on control over the entire project, from start to finish. The following blog will help you understand “what is PRINCE2” and “why PRINCE2” is such a popular and frequently utilized technique in project management.
Let us begin the blog by answering the main question of today’s agenda, which is, “What is PRINCE2?”
What is PRINCE2?
PRINCE2, or Projects In Controlled Environments, is a well-known project management system. It’s a systematic approach to project management that emphasizes organization and control. Every project begins with a detailed project plan, each stage is organized, and any loose ends are tied up once the project is completed. But, in practice, what does PRINCE2 project management entail? Continue reading to learn about the approach’s core ideas of this methodology.
PRINCE2 was built by 150 different European organizations and launched in 1996. This breadth of knowledge and experience resulted in a straightforward yet adaptable approach to project management. As a result, PRINCE2 project management has now been custom-made to fit businesses and organizations in various industries. Furthermore, continual updates have guaranteed that the PRINCE2 methodology has remained relevant as markets, sectors, and business practices have evolved.
PRINCE2 can help individuals and companies navigate project management essentials, regardless of their size or scope. Throughout the project, it provides a framework that focuses on structure and control. Therefore, to support efficient resource management and regular progress monitoring, PRINCE2 breaks projects into manageable stages.
PRINCE2 Terminology
PRINCE2 is “product-based,” which means that project plans are focused on producing results rather than merely scheduling activities; processes cover all aspects of a project, from conception to completion. So, every project begins with a project plan, and each project stage is well-structured. Further, it establishes a common vocabulary throughout a project and establishes contract breakpoints.
Regardless of the type or scope of the project, PRINCE2 assists project managers in dividing projects so that each stage is more manageable and controllable. It’s quite adaptable and may be tailor-made to meet your individual needs. You may plan your project properly before you start working on it with the help of PRINCE2. As a result, from beginning to end, the procedure is well-structured. It also helps in completing the project by tying up any loose ends.
Now that we know the term “PRINCE2”, we shall jump into the next topic, “PRINCE2 Benefits.”
Why Is PRINCE2 Important?
PRINCE2 benefits project managers, directors, and an organization by allowing for more control over resources and managing business and project risk more effectively. Therefore, PRINCE2 represents well-established and tested best practices in project management. Following, we have listed a few of the benefits of PRINCE2.
1. Get Into the Project Management Domain
PRINCE2 is the industry standard for project management. It teaches you the skills you need to be confident in managing projects successfully. This is because PRINCE2 employs a common language, systems, and procedures. As a result, this gives you more control over your resources and risks.
2. Enhances Your Knowledge Flexibility
PRINCE2 is a best practice method custom-made to the specific needs of different organizations for all projects, including Agile delivery. Hence, whatever your typical projects entail, PRINCE2 can handle them. In addition, you can gradually create a more bespoke and subjectively appropriate approach to project management for your organization by learning as you apply and tailor the framework.
3. Improve Employment Prospects
A PRINCE2 certification is an excellent addition to your resume. PRINCE2 is a world-class international product and the industry standard for project management. PRINCE2 certification is held by more than half of those who responded to Arras People’s 2011 survey. So it’s no surprise that many companies worldwide require PRINCE2 certification for their employees.
4. A Best Practice Framework
PRINCE2 is more than just a theory. The methodology is founded on practitioners’ expertise and practical knowledge from numerous industries and sectors. It also has a track record of success, with plenty of case studies to back up the efficacy of PRINCE2 best practices.
5. Common Language
PRINCE2 is an organized and controlled start, ensuring a valid reason for the project and all people and resources are organized. Therefore, they are ready for the project with good communication among the project management team, stakeholders, and the rest of the organization.
PRINCE2 has now been in use for several decades. Therefore, it has gained widespread recognition and acceptance, with a global community of practitioners familiar with the framework’s common terminology and methods.
After understanding PRINCE2’s advantages, let us look into the “key elements of PRINCE2.”
Key Elements of PRINCE2
PRINCE2 project management is a process-based approach that focuses on project organization and control from start to finish. That means projects are meticulously planned before they begin, each stage of the process is clearly defined, and any loose ends are neatly tied up once the project is completed. Moreover, the key elements of the methodology are principles, processes, and themes. Let us now discuss each of them briefly.
PRINCE2 Principles
The PRINCE2 principles are universal and can be applied to all projects, self-validating. They have been demonstrated in practice over many years and empowering. Therefore, they provide practitioners of the approach with increased confidence and capacity to influence how the project is managed. In addition, these principles are derived from lessons learned from successful and unsuccessful projects and provide a foundation for good practice for those involved. When managing a project, the principles are followed to meet the standards of PRINCE2. Let us now go through all the seven principles in detail:
1. Continued Business Justification
The business justification is frequently documented in some business cases in most firms. During the project initiation, some organizations may utilize business plans or similar documents as the business reason, even though these documents may not meet the requirements of a business case. Therefore, the format and formality depend on corporate standards, needs, and circumstances, and documentation may differ.
2. Learn From Experience
The PRINCE2 project management methodology places a high value on team learning. At each stage of the project, teams should note the key lessons learned and ensure that they are implemented in later stages or even future projects.
3. Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Members of the project can take on multiple roles or share a single role. Therefore, the structure of people in a project is divided into four levels: corporate, project board, project manager, and team.
4. Manage by Stages
The PRINCE2 methodology divides each project into distinct project management phases, and at the end of each phase, phase outcomes and lessons learned are recorded. This also aids in keeping track of where the project is heading.
5. Manage by Exception
Each project objective has what is known as tolerances. This establishes boundaries and defines how authority is delegated. For example, if the tolerance is exceeded, the management team must decide whether or not the tolerance is to be redefined.
6. Focus on Products
Teams must ensure no misalignment between project deliverables and project requirements. Consequently, the teams must constantly check and measure the quality of the deliverables to achieve this.
7. Tailor to Suit the Project
The PRINCE2 Methodology allows the approach for different projects to be custom-made, built on the available resources and time. Different parameters, such as the number of team members and the amount of oversight and planning for each project phase, are custom-built to meet the client’s needs.
PRINCE2 Themes
The PRINCE2 themes highlight aspects of project management that are addressed regularly as the project moves through its lifecycle. Throughout the project lifespan, for example, the business justification for the project will need to be updated and revalidated, change will occur, and risks will need to be handled. Following are the themes of PRINCE2:
1. Business Case
The project begins with a concept that is thought to have potential value for the organization. So, this subject focuses on how a concept becomes a viable investment offer for the business and how project management keeps the project focused on the organization’s goals throughout.
2. Organization
The project’s chartering organization must assign the work to managers responsible for it and oversee its execution. Because project teams are cross-functional and developed specifically for the project, standard organizational structures outside the project team may not apply. Moreover, this topic outlines the tasks and responsibilities of the temporary PRINCE2 project management team needed to manage the project properly.
3. Quality
Only a broad outline of the first concept is grasped. This subject outlines how the outline is created so that all parties know the product quality qualities to be supplied and how project management will ensure that these needs are met.
4. Plans
PRINCE2 projects are organized around a set of authorized blueprints. However, this theme adds to the quality theme by explaining the procedures involved in developing plans and the PRINCE2 approaches that should be used. In addition, the plans in PRINCE2 are custom-made to the needs of individuals at all company levels. Throughout the project, they are the focal point for communication and control.
5. Risk
Projects usually carry a higher level of risk than regular operating operations. Therefore, this theme focuses on how project managers deal with uncertainty.
6. Change
This subject outlines how project management evaluates and responds to concerns that may influence any of the project’s baseline aspects (its plans and completed products). Therefore, unexpected general problems, demands for adjustment, or instances of a product failing to match its specifications are examples of issues.
7. Progress
This subject focuses on the plans’ long-term viability. Therefore, the theme outlines the approval procedure for plans, monitoring actual performance, and the escalation process if things don’t go as planned. In conclusion, the progress theme will define whether and how the project will move forward.
PRINCE2 Process
The processes describe a progression from the pre-project activity of getting started to the project lifecycle stages and the final act of project closure. Therefore, each process includes a suggested activities, products, and responsibilities checklist. Following are the procedures of PRINCE2:
1. Starting Up a Project
Before the project begins, the very first procedure of the project is aka the Pre-Project Process. First, the project’s goals are defined, forming a project management team. Moreover, the responsibilities involved in creating the project brief and stage plan for the pre-project stage are project managers and executives.
2. Directing a Project
Authorizing project stages and administering the project from start to finish (by Exception) are the main functions of this particular PRINCE2 process. Consequently, the Board of Directors for the Project is responsible for functioning in this domain.
3. Initiating a Project
The project has officially started in this “Initiating a Project” process. The project’s products define (including quality, time, cost, risk, and resources.) Moreover, roles responsible for Project Initiation Documentation (including Project Plan & Business Case) include project manager and executive.
4. Controlling a Stage
Each project stage monitors the project status and controls it with corrective actions/exception escalations. In addition, roles are responsible for communicating project-related information to stakeholders: Manager of the Project.
5. Manage Product Delivery
Checkpoint Reports are used to report on the execution of Work Packages and the creation of scheduled project products to the Project Manager. Again, the Team Leader is the responsible person here.
6. Managing a Stage Boundary
The End-Stage Report and Stage Plan are used to report on the current stage’s performance and plan the following stage (and whether to continue the project.) So, the board of directors for the project is responsible for looking after the managing stage.
7. Closing a Project
Responsibilities are accountable for completing the project with an end project report and a Lessons Learned Report. Consequently, the Board of Directors is responsible for the project.
After understanding the “Key Elements of PRINCE,” let us switch our attention to “PRINCE2 Roles.”
Roles Under PRINCE2 Methodology
PRINCE2 is one of the most widely used project management methodologies today. PRINCE2 is based on the concept of project roles. Therefore, the method specifies nine filled roles, even if the same person fills multiple roles. The following are the roles under the PRINCE2 methodology:
1. Executive
The executive secures project funding and maintains the project’s business case and justification. However, they accept the project’s deliverables and focus on the project’s benefits to the organization or the program or portfolio that the project is a part of, similar to a “project sponsor” in other methodologies. So, the executive appoints the project board and project management team.
2. The Senior Use
This represents the organization or people who will use the PRINCE2 project’s product or service. Those who will affect by it directly. The customer and the user may be the same. In addition, the senior user ensures that the Project Board respects the user’s needs and that these are specified in the project.
3. Senior Supplier
The suppliers are all individuals and organizations who carry out the project work, i.e., those who create the project’s deliverables. It consists of internal (the project team) and external (suppliers). It may also include those who will support and maintain the products after the completion of the project.
Firstly, the senior supplier represents the suppliers’ interests. Secondly, suppliers typically want to be fairly compensated for their efforts and receive a positive reference for future work. In addition, work satisfaction ranks high on the list as well.
4. Project Manager
The project manager oversees the project’s planning, execution, controlling, and closure phases. So, project managers form a project team and keep track of its progress. In addition, they make a project plan that includes a timeline and a budget and communicate with the project team and customers.
5. Team Manager
The Team Manager is a lower-level manager in charge of the project’s deliverables daily. They are responsible to the project manager. They may have a large project team supporting them or do all of the work themselves, but they are the technical experts.
The team manager creates work packages, which are then assigned to project team members for completion. A series of work packages is transformed into a management stage.
6. Project Assurance
At predetermined intervals, Project Assurance provides an independent assessment of project progress. The Project Board commonly fills this role, which must be independent of the Project Manager. The Project Board may, however, appoint an independent Project Assurance team. Moreover, this team is responsible for keeping the project on track with business assurance, user assurance, and supplier assurance.
Now, we shall get to know more about “PRINCE2 Certification.”
PRINCE2 Certification
Any project manager’s goal is to complete projects on time, within budget, and within scope. So, PRINCE2 walks you through a project’s lifecycle stages, giving your project structure and a common language. In addition, it embodies the “how-to” of project management. It is adaptable, scalable, and can be customizable to meet your specific needs.
PRINCE2 is based on the tried-and-true experience of project management practitioners worldwide. In conclusion, it provides the themes, principles, and processes needed to deliver successful projects of any size and complexity.
Why PRINCE2 Certification?
PRINCE2 Certifications, or Projects in Controlled Environments, Version 2, are among the most popular Project Management certifications worldwide. One of the most significant benefits of certification is improving your project management skills. Rather than being an instructional manual, it emphasizes understanding and embodying a set of project management principles.
This PRINCE2 teaches you how to successfully manage multiple projects across the board by utilizing logic and processes. As a result, the PRINCE2 certification is now a globally well-known certification with over 1,000,000 professionals. It has a wide range of roles and sectors and 18 languages spoken in more than 150 countries.
Now, the following pointers shows some reason that proves why PRINCE2 certification is necessary:
◉ PRINCE2 is a popular credential that can broaden your career prospects in project management and help you move into senior roles
◉ Enhances your project management skills and showcases your commitment to your chosen field of project management
◉ Acquire the ability to evaluate your teammates better and educate them to manage projects successfully
◉ Gain monetary benefits, better assignments, and enhances your career opportunities
◉ Learn about managing projects and how to work in a project environment by implementing a globally-recognized method
◉ Become a part of a fast-growing industry with more than 1,000,000 PMP certification holders worldwide
◉ Helps you to contribute to your company’s growth, and performance and add value to your organization
◉ Equips you with the deep knowledge to efficiently & effectively execute any project
◉ Provides a roadmap for businesses to finish projects within scope, timeframe, and budget
◉ Provides a fresh perspective on projects and how they fit with the organizational business strategy
◉ Improved communication and better utilization of business resources
◉ Enhanced effectiveness in delivering project deliverables consistently
◉ Increases agility and stability of ongoing business-critical projects
How to Get PRINCE2 Certified?
PRINCE2 certifications are widely famous as the leading project management qualification for project management professionals worldwide. Therefore, it’s no surprise that many aspiring project managers are eager to learn PRINCE2 and advance their careers. So, whether you’re a seasoned project manager looking to brush up on your skills or a newcomer to the industry, we’re here to answer any questions you might have about PRINCE 2 and PRINCE2 project management.
PRINCE2 Foundation
This certification introduces the PRINCE2 method and aims to confirm that a person is familiar with and understands the PRINCE2 method well enough to implement it in a PRINCE2-enabled environment. Moreover, professionals who want to take up Practitioner certification, which is the next level, require this certification as well.
PRINCE2 Practitioner
This certification is for project management practitioners who want to advance their careers and improve their knowledge of the PRINCE2 Methodology. So, the PRINCE2 Practitioner certification exam assesses a professional’s ability to manage non-complex projects across all streams.
PRINCE2 Agile
The PRINCE2 Agile qualification is of two levels: Foundation and Practitioner. PRINCE2 Agile teaches the fundamentals of combining PRINCE2 with agile methodology. This allows for scalability as well as integration with corporate management processes. In addition, this certification is mainly for project management professionals who already have PRINCE2 credentials and are looking for additional guidance on using the agile methodology. This certification is appropriate for industries of any domain and scale. Above all, it offers scalability and the ability to integrate with corporate management processes.
We at Invensis Learning will provide 4-Days live Instructor-led PRINCE2 Certification accredited by AXELOS and provide live online training and PRINCE2 Certification Exam cost. In addition, the two PRINCE2 project management certifications levels – PRINCE2 Foundation & PRINCE2 Practitioner will be covered in training.
Know the Requirements
Eligibility Criteria
The PRINCE2 Foundation certification exam has no prerequisites.
To sit for the PRINCE2 Practitioner exam, you must have passed any of the following exams:
◉ PRINCE2 Foundation
◉ Project Management Professional (PMP)
◉ IPMA Level C® (Certified Project Manager)
◉ Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) IPMA Level A® (Certified Projects Director)
◉ IPMA Level B® (Certified Senior Project Manager)
◉ IPMA Level D® (Certified Project Management Associate)
Who Should Attend?
Jobs that can benefit from PRINCE2 certification include:
◉ Project Managers
◉ Aspiring Project Managers
◉ Project Board members
◉ Product Delivery Managers
◉ Project Support Staff
◉ Operational Line Managers
◉ Team Leads / Team Managers
To gain the required knowledge and requirements, you have to take up training from any trusted bodies. However, as already mentioned, we at Invensis learning will provide training for PRINCE2 Certification. In addition, the PRINCE2 Certification training cost is approximately 700 USD to 1500 USD. So, for more details, please refer to the training schedule given below. Then, select your preferred date and enroll in the PRINCE2 course.
Invensis Learning offers a live virtual instructor-led corporate training program tailored to enterprise teams looking to train their employees on specific aspects of their job processes or responsibilities. So, our expert certified trainers will enhance your learning curve and enable your teams to use their skills to meet industry standards through corporate training.
Attend the Exam
Exam Format
The following is the exam format for the PRINCE2 Foundation:
| Exam Duration | 60 Minutes |
| No. of Questions | 60 |
| Passing Criteria | 55% |
| Exam Type | Closed Book |
The following is the exam format for the PRINCE2 Practitioner:
| Exam Duration | 60 Minutes |
| No. of Questions | 60 |
| Passing Criteria | 55% |
| Exam Type | Closed Book |
Renewal and Maintenance of credentials
| Exam Type | Objective Testing |
| No. of Questions | Three questions: 10 items per question, each worth one mark |
| Passing Criteria | 17 marks or more are required to pass (out of 30 available): 55% |
| Duration | One hour’s (60 minutes) duration, no additional reading time |
Wednesday, 28 December 2022
The Fully Credentialed Data Science Professional
Monday, 26 December 2022
Sitting Down with John Linford- Security & OTTF Forum Director, The Open Group
Please can you tell us how long you have been in your role and what you enjoy most about it?
What has your journey with The Open Group been like so far?
Are there any new updates within your Forum that you can share?
Can you tell us about any exciting updates planned within your Forum?
What are you most looking forward to for the year ahead?
Is there any advice you can give for those looking to start in the industry?
If you could give advice to your respective self before starting in your role, what would it be?
Friday, 23 December 2022
How to Crack ITIL 4 Foundation Certification Exam 2022?
What is ITIL 4 Foundation Certification?
Who Should Get ITIL 4 Foundation Certification?
What is ITIL 4 Foundation Exam?
How Difficult is the ITIL 4 Foundation Exam?
Tips on How to Crack the ITIL 4 Foundation Exam
Additional Hints to Ace the ITIL 4 Foundation Exam
Wednesday, 21 December 2022
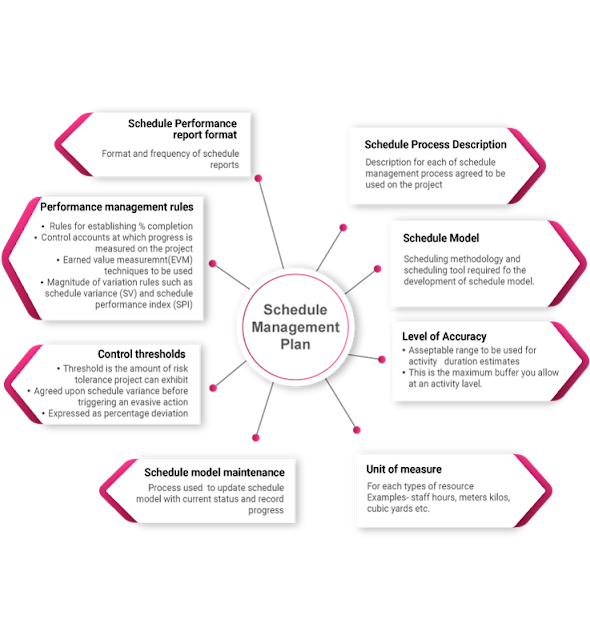
Project Schedule Management: How to Plan, Develop, Maintain & Control?
What is Schedule Management?
Project Schedule in Project Management? Explained!
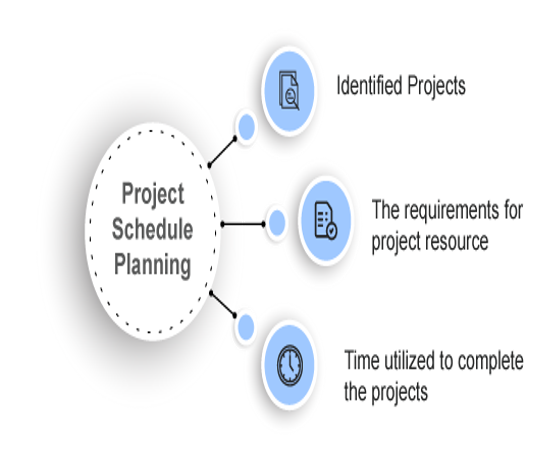
Project Schedule Planning in Project Management
Develop Project Schedule in Project Management!
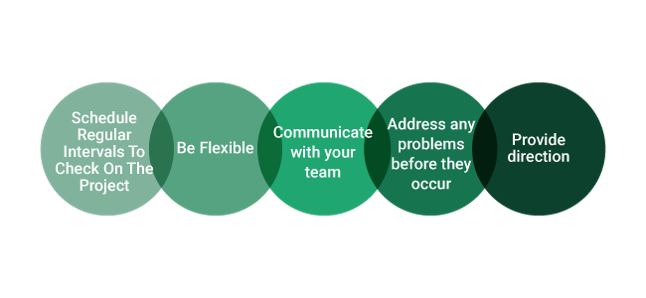
5 Steps That Help to Develop a Schedule in a Project
How to Develop a Project Schedule?
| What To Do? | How To Do It? |
| Determine the tasks to be placed in the schedule | Refer to the tasks identified in the work breakdown structure. |
| Determine the relationships between the tasks | Identify tasks that must be completed before other tasks can begin. Identify tasks that can be done while other tasks are being performed. - A network diagram (a precedence diagramming method) can be used to diagram the dependencies. |
| Assign each task to a specific staff | This establishes ownership of the task. Assigning the right person to the right task is one of the most critical factors in a project’s ultimate success. |
| Estimate the amount of effort required for each task |
Work with individual team members or others who have experience with this type of project. Document assumptions used in estimating. |
| Consider the other variables that go into building the schedule | Example variables to consider: - Project Constraints - Assumptions - Lead and lag time (delay) of materials - When, where, or how the task must be performed - Project risks - The realities of vacations, meetings, discussions, staff interactions, and any ongoing responsibilities team members may have. - Staff Training time |
| Build a time reserve into the schedule for contingencies and unforeseen events |
A contingency is a specific provision for unforeseeable elements that could cause schedule delay. - The degree of acceptable risk for delays A good rule of thumb for schedule contingency is 20%, but a project can include more or less based on the factors above. |
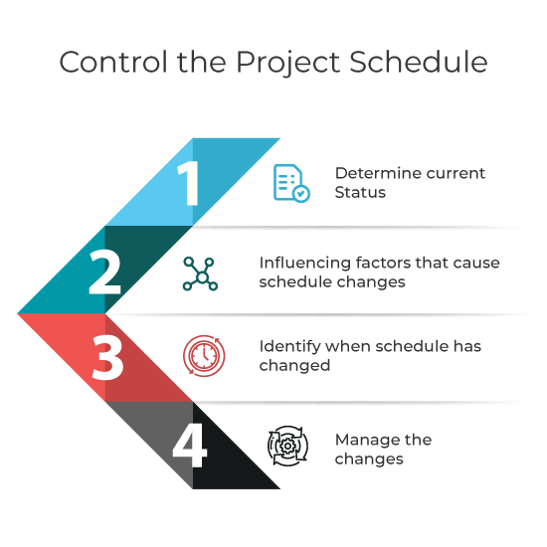
| Identify the project’s critical path |
The critical path is a project management technique that analyzes what activities have the least amount of scheduling flexibility (i.e., are the most important) and then predicts project duration based on the activities that fall along the “critical path.” If the critical path exceeds a required deadline, review methods to shorten the critical path. |
| Check to see if the staff is over-allocated |
If the staff is over-allocated, figure out a way to level the team so they are assigned the right amount of work. - Modify the schedule to accommodate the constraint Caution: There is an overhead cost for bringing new staff up to speed. Not all team is truly interchangeable. The skill level of the new person may affect the time to complete and the quality of the work. Contract staff may need more oversight. |
| Repeat steps 3 and 5-8 until a baseline is established. | Developing the project schedule is an iterative process. |
| Place the schedule information in a Gantt chart |
Place the tasks, milestones, relationships, staff assigned, duration, and work estimates in a Gantt chart to show the detailed timing of the project. Various project management tools can generate Gantt charts. Other formats can be used to display the schedule information based on the needs and preferences of your customer. |