There are 5 stages of ITIL lifecycle: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation and Continual Service Improvement.
They form the perfect ITIL Service Management plan. Each stage covers different content and the ITIL process that needs to be in place for the operations within each stage to work properly. Without the ITIL process and accompanying content, the stage is likely to fail and all the other stages will crumble down with it. It is important that the IT service manager is knowledgeable about each ITIL process and that the service owner knows how to implement each of the stages’ processes as he ultimately takes ownership of the service and its lifecycle. Aspects of roles and responsibilities such as the service owner are covered in the ITIL Foundation Certification course.
Service strategy is the core stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. Without a solid IT strategy that is aligned with the organization’s business strategies, an IT service is unlikely to succeed. The ITIL process followed during this stage makes all the other stages possible and provides direction for the stages that follow.
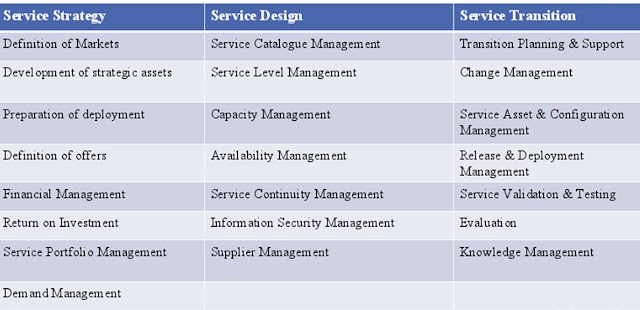
The Service Strategy stage cover: the definition of markets, development of strategic assets, preparation of deployment, and definition of offers. The service strategy stage provides the initial link between business strategies and IT strategies of the organization. The Service Strategy stage further includes financial management, return on investment, service portfolio management and demand management processes.
They form the perfect ITIL Service Management plan. Each stage covers different content and the ITIL process that needs to be in place for the operations within each stage to work properly. Without the ITIL process and accompanying content, the stage is likely to fail and all the other stages will crumble down with it. It is important that the IT service manager is knowledgeable about each ITIL process and that the service owner knows how to implement each of the stages’ processes as he ultimately takes ownership of the service and its lifecycle. Aspects of roles and responsibilities such as the service owner are covered in the ITIL Foundation Certification course.
ITIL Process #1: Service Strategy
Service strategy is the core stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. Without a solid IT strategy that is aligned with the organization’s business strategies, an IT service is unlikely to succeed. The ITIL process followed during this stage makes all the other stages possible and provides direction for the stages that follow.
The Service Strategy stage cover: the definition of markets, development of strategic assets, preparation of deployment, and definition of offers. The service strategy stage provides the initial link between business strategies and IT strategies of the organization. The Service Strategy stage further includes financial management, return on investment, service portfolio management and demand management processes.
ITIL Process #2: Service Design
The Service Design stage in the ITIL Process is the planning and design phase of IT strategies. Ideas are formed out of inspiration drawn from IT strategies, be it new services or updates on existing services. New services are planned and designed in service design stage in order to achieve the business vision and strategy of the organization. The successful design of an IT service will ensure that the service can transition successfully into a live environment and deliver on customer expectations.
The Service Design stage includes service catalog management, service level management, capacity management, availability management, service continuity management, information security management and supplier management processes. The IT service owner should be familiar with all these processes and be able to effectively manage the ITIL process with the guidance of the IT service manager.
ITIL Process #3: Service Transition
The Service Transition stage in the ITIL Process is the phase where designed new services or changed services are built, tested, implemented, verified and transferred into operations. The Service Transition stage is the key step during which an idea seed is planted in soil where it can grow to fruition.
The Service Transition stage includes transition planning and support, change management, service assets and configuration management, release and deployment management, service validation and testing evaluation, and knowledge management processes. Change management is especially important if an existing service is being modified.
ITIL Process #4: Service Operation
The Service Operation stage in the ITIL Process is the phase where designed services are put into a live environment and end customers start to use services of the organization. This is the make of break phase where consumers finally interact with the service. If each ITIL process were followed correctly, the service is likely to delight the customer and succeed as a service. However, this stage has its own processes that need to be managed: event management, incident management, request fulfillment, problem management and access management processes. Any ITIL process that is neglected in this stage will lead to customers being disappointed which could lead to loss of sales.
ITIL Process #5: Continual Service Improvement
The Continual Service Improvement (CSI) stage in the ITIL Process binds all other four service lifecycle stages together and aims to identify and analyze the improvement points in these stages and then implement the improvement plans to mitigate any points of pain in the processes. CSI stage includes 7 Step improvement process, service reporting, service measurement, return on investment for CSI, the business questions for CSI and, service level management processes respectively. The CSI process is the shell that protects each ITIL process and the effective usage of efficient CSI processes will result in a service with longevity in the market.
Proper IT Service management throughout the service lifecycle is of critical importance if a service is to be successful. There are many processes to be designed, optimized and followed, each associated with a specific step in the ITIL service lifecycle. An ITIL process is a cog in the machine that is the ITIL service lifecycle. A poor ITIL process or incorrectly followed processes can easily cause damage that may ultimately lead to customer dissatisfaction.






0 comments:
Post a Comment