Managing a project often feels tough. The complexity can be overwhelming, with various tasks needing alignment and constant updates that are essential for team coordination. This is where the role of precise project estimates becomes crucial, yet it’s a task that’s often as challenging as the project itself.
The solution? The project manager’s best ally is the project timeline. It is a schedule for the project that has information related to what tasks need to be accomplished and when. It keeps you on track with the overall project flow. Without a project timeline, the risk of a project spiraling into chaos is high, and chaos is always desirable.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of project timelines. You’ll discover what they are, why they’re beneficial, and how to use top-tier project management software to create them more effectively.
What is a Project Timeline?
A project timeline is a visual and chronological depiction of a project’s workflow. It outlines the various tasks involved and their respective dependencies, durations, and deadlines. This timeline plays a pivotal role in successful project management as it provides a clear and comprehensive overview of everything that needs to be done and the timeframe within which these tasks must be completed.
Project timeline is a crucial tool for everyone involved in the project. The timeline offers a snapshot view, allowing team members to assess what has been completed quickly, gauge the current progress, and understand what remains to be done. In essence, it serves as a roadmap, detailing the project’s past, present, and future.
Importance of Project Timeline
A project timeline isn’t just a tool; it’s a compass guiding project managers and their teams through the complexities of their tasks. It’s an essential component of the project management concept, offering a visual pathway and aligning tasks to support stakeholders and ensure success.
Here’s a closer look at the benefits a project timeline offers:
Identification of Cost and Time
Before a project starts, a well-crafted timeline helps assess the necessary resources, costs, and time needed for completion. This foresight is invaluable for maintaining customer satisfaction, as it aids in communicating and setting realistic expectations regarding costs and timelines with clients.
Reveals a Clear Path Forward
In projects brimming with complexity, a project timeline simplifies the roadmap. It distinctly shows the first steps and the subsequent actions needed, eliminating confusion and streamlining the process.
Facilitates Project Analysis
A timeline provides a dynamic view of the project’s progression, making it easier to spot when changes are needed. For instance, if a deadline is missed, the timeline can be adjusted accordingly, ensuring that dependent tasks are realigned. It’s a tool for analyzing past actions, managing present tasks, and strategizing for future improvements.
Tracks Task Hierarchy and Sequencing
Understanding which tasks need to precede others is critical in project management. The timeline lays out this hierarchy clearly, ensuring all activities are carried out correctly.
Ensures Unified Goals
For a project to succeed, team alignment is crucial. A project timeline clarifies each team member’s role and how they contribute to the overall objectives, promoting a unified approach towards the project’s goals.
Enables Clear Communication
With a shared timeline, the project manager, team members, and clients can easily track the current progress and upcoming tasks. This transparency simplifies communication and facilitates the efficient management of the project.
Fosters Teamwork
A project timeline encourages teamwork by highlighting task dependencies, due dates, and progress. It makes every team member aware of their impact on the project and how their work interlinks with others, fostering a collaborative environment.
Keeps Everyone Informed
A well-maintained timeline keeps all stakeholders informed about the project’s progression. This builds trust and streamlines communication, making managing expectations and responding to inquiries easier.
A project timeline is more than just a schedule; it’s a strategic tool that brings clarity, efficiency, and teamwork to the forefront of project management. By leveraging its benefits, project managers can navigate through the complexities of their projects with greater ease and effectiveness.
Types of Project Timeline
When it comes to project timelines, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Different projects have unique requirements, and choosing the right type of timeline is essential for effective project management.
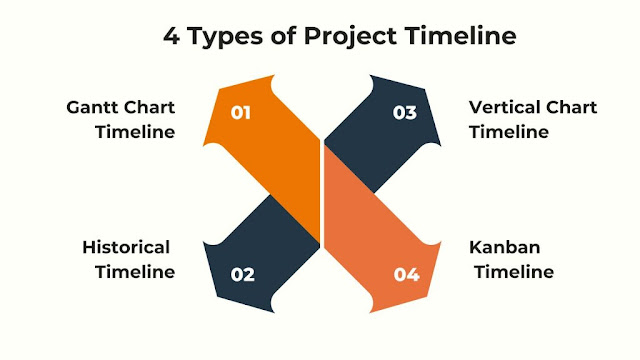
Here are four common types of project timelines, each with its own set of advantages :
Gantt Chart Timeline
A Gantt chart timeline visually represents tasks like pouring the foundation, framing, electrical work, and plumbing. It clearly shows each task’s start and end dates, dependencies between tasks, and who is responsible for each.
Pros: Gantt charts offer a comprehensive overview of the entire project, making tracking key milestones and task dependencies easy. Modern Gantt charts are highly interactive, allowing real-time updates and edits.
Historical Timeline
A historical timeline arranges project tasks chronologically, from left to right or top to bottom, similar to a history timeline showcasing key dates from a specific period.
Example: In a software development project, a historical timeline could display the sequence of development phases, such as requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and deployment.
Pros: Historical timelines provide a straightforward chronological view of project tasks, making it easy to understand the order in which activities should be completed.
Vertical Chart Timeline
A Vertical Chart Timeline is ideal for tracking data-centric projects, displaying trends and changes over time, such as monthly website traffic or recurring revenue growth.
Pros: Vertical chart timelines are ideal for data analysis or continuous tracking projects. They effectively illustrate trends and changes over time.
Kanban Timeline
A Kanban timeline can be used alongside a Gantt chart. It helps prioritize daily or weekly tasks, ensuring team members are clear about what needs to be done immediately.
Pros: Kanban timelines are a hybrid solution combining task prioritization elements with a Gantt-like approach. They are particularly useful for teams needing high-level project tracking and day-to-day task management.
Selecting the right type of project timeline depends on the nature of your project and the level of detail and tracking required. Whether you opt for the comprehensive view of a Gantt chart, the chronological simplicity of a historical timeline, the data-driven approach of a vertical chart, or the task management focus of a Kanban timeline, choosing the right tool will significantly enhance your project management capabilities.
How to Create a Project Management Timeline?
A well-crafted project management timeline is the backbone of any successful project. It provides clarity, structure, and a roadmap for the entire team.
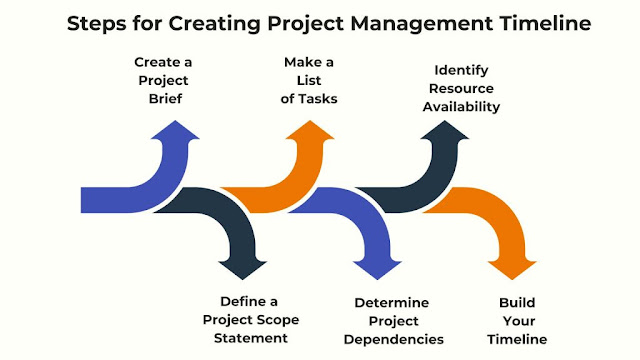
To create an effective project management timeline, follow these essential steps:
Create a Project Brief
A project brief is the foundational document that sets the stage for successful project management. It is a compass guiding all project stakeholders towards a common goal.
Here’s how to create an effective project brief:
Why Start with a Project Brief?
A project brief clearly explains the purpose, objectives, milestones, and overall vision. By answering key questions in the project brief, you ensure that everyone involved is on the same page.
Key Questions to Address in Your Project Brief:
- Project Goals: What are the primary goals of the project? Define both the internal and external objectives you aim to achieve. Clearly articulate what success looks like.
- Project Deliverables: What are the tangible outcomes or products the project will produce? These are the results that stakeholders can expect at the end of the project.
- Stakeholders: Identify the internal and external stakeholders involved in the project. Define their roles and responsibilities. Understanding who is involved is critical for effective collaboration.
- Project Timeframe: Specify the project’s timeline. Highlight the most important dates, including the project’s start and end dates. This sets the project’s temporal boundaries.
- Project Scope: Describe the project’s scope in detail. If you have a formal project scope statement, reference it here. Clearly state what is included in the project and, equally important, what is not.
- Key Milestones: Identify the key milestones of the project. Milestones are significant events or achievements that mark progress. They provide a sense of accomplishment as the project unfolds.
Starting your project with a well-structured project brief ensures that everyone involved understands the project’s objectives, scope, and timeline. It sets the stage for effective planning and execution, helping to keep the project on track from start to finish.
Define a Project Scope Statement
Before embarking on any project, defining its scope through a clear and comprehensive project scope statement is essential. This statement outlines the boundaries and objectives of the project and serves as a guiding document throughout the project’s lifecycle.
What is a Project Scope Statement?
A project scope statement is a detailed document that defines the project’s scope, including what is included in the project and, equally important, what is not. It clearly and concisely describes the project’s deliverables, objectives, constraints, assumptions, and acceptance criteria.
Components of a Project Scope Statement
- Project Objectives: Clearly state the project’s objectives and what you aim to achieve. These objectives should align with the overall goals of the project.
- Deliverables: Describe the tangible outcomes or products that the project will produce. These are the results that stakeholders can expect at the end of the project.
- Scope Description: Provide a detailed description of the project’s scope, including the boundaries and limitations. What is within the project’s scope, and what is excluded?
- Constraints: Identify any limitations or restrictions that could impact the project, such as budget constraints, time constraints, or resource limitations.
- Acceptance Criteria: Define the criteria that must be met for the project to be considered complete and successful. These criteria should be measurable and specific.
Example of a Project Scope Statement
Consider a technical project to develop a website for a client:
- Project Objective: To create a fully functional e-commerce website for the client’s online business.
- Deliverables: A responsive e-commerce website with features including product listings, a shopping cart, secure payment processing, user registration, and order tracking.
- Scope Description: The project encompasses website design, front-end and back-end development, database integration, and testing. It does not include digital marketing services or ongoing website maintenance post-launch.
- Constraints: The project budget is limited to $50,000, and the website must be live within four months to align with the client’s marketing campaign.
- Acceptance Criteria: The website is complete when all specified features are fully functional, thoroughly tested, and approved by the client.
Creating a project scope statement tailored to your project’s technical aspects ensures that all stakeholders share a common understanding of the project’s scope and objectives. This document is a vital reference for effective project planning, execution, and successful project delivery.
Make a List of Tasks
To create a successful project timeline, you must compile a comprehensive list of tasks spanning from the initial project planning phase to the final deliverable, whether a report, an event, or a technical project.
This task list should encompass major milestones and smaller steps that collectively contribute to completing the project on time and within the budget.
During this phase, the order of tasks is not a primary concern; the focus is on identifying all necessary activities. Here’s how to effectively create a task list:
Comprehensive Task List
Break it Down: Break down the project into its constituent tasks. Consider major actions and finer details, ensuring everything is noticed.
Example Task Breakdown: Considering the previous example, if we break the tasks, it will be as follows:
Project Initiation
- Define project objectives and scope
- Assemble the project team
- Identify key stakeholders
- Create a project brief
Requirements Gathering
- Meet with the client to gather website requirements
- Define user stories and use cases
- Document functional and non-functional requirements
Design Phase
- Create wireframes and mockups
- Design the website’s user interface (UI)
- Develop a visual design concept
- Obtain client approval on designs
Development
- Set up the development environment
- Build the website’s front-end
- Develop back-end functionality
- Integrate a secure payment processing system
- Implement user registration and login features
Database Integration
- Design the database schema
- Develop database tables and relationships
- Implement data storage and retrieval functions
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Perform unit testing for code components
- Conduct integration testing
- Test website functionality (e.g., product search, cart)
- Perform security testing and vulnerability assessment
- Identify and resolve defects and issues
Deployment
- Prepare the website for production
- Deploy the website to a web server
- Configure domain and hosting settings
- Perform final testing in the production environment
User Training
- Train client personnel on website administration
- Provide user manuals and documentation
Client Acceptance
- Review the website with the client
- Address any final client requests or adjustments
- Obtain client sign-off on the website
Launch and Marketing
- Plan and execute the website launch
- Implement digital marketing strategies
- Monitor website performance and user feedback
Post-launch Maintenance
- Establish a maintenance plan
- Provide ongoing support and updates
- Address any issues or bugs that arise
Subtask Breakdown
For longer or more complex tasks, further divide them into smaller, manageable subtasks. This clarifies the scope of each step and ensures that no minor detail is overlooked. It makes tackling complex tasks more achievable.
Creating a detailed task list lays the groundwork for efficient project planning and timeline development. Subsequent steps will involve organizing these tasks in the right sequence and assigning timeframes to each, ensuring that your project progresses smoothly from start to finish.
Determine Project Dependencies
As your project progresses, you may encounter tasks that can be worked on simultaneously, keeping your team members independently engaged. However, there will come a point where certain tasks depend on the completion of others. Identifying and managing these task dependencies is crucial for efficient project execution.
Why Define Task Dependencies?
Mapping out task dependencies in advance can save valuable time in the long run. It allows for adequate time allocation to each step and helps prevent bottlenecks. Moreover, it’s essential to provide team members with a clear understanding of when they might need to wait for another task to be completed, enabling better schedule planning.
Task Dependencies in e-Commerce Website Creation
In the context of creating an e-commerce website, here are some task dependencies to consider:
Design Approval Before Development
1. Dependency: The design phase must be completed and approved before the development phase can begin.
2. Reasoning: Developers need finalized designs to implement the website’s user interface accurately.
Database Integration Before Functionality Development
1. Dependency: The database integration phase must precede the development of website functionality.
2. Reasoning: Functionality development relies on access to the database for tasks like product listing and user account management.
Testing After Development
1. Dependency: Development tasks must be finished before testing can commence.
2. Reasoning: Testing requires a stable and functional website to identify and resolve defects effectively.
Client Review and Sign-off Before Launch
1. Dependency: The client’s review and approval are necessary before launching the website.
2. Reasoning: Client approval ensures that the website meets their requirements and expectations.
Maintenance Planning Concurrent with Development
1. Dependency: Planning for post-launch maintenance should start in parallel with website development.
2. Reasoning: Maintenance planning should be considered from the project’s inception to ensure seamless post-launch support.
By defining task dependencies like these, you can establish a logical sequence of activities, allocate resources efficiently, and communicate effectively within your project team. This proactive approach minimizes delays, enhances project coordination, and contributes to the successful completion of your project, whether it’s an e-commerce website or any other endeavor.
Identify Resource Availability
One of the critical factors in an effective project timeline is identifying the availability of your project team members or employees. While the estimated task duration may be relatively short, you must consider when team members can allocate their time to work on assigned tasks.
Resource availability, particularly the availability of human resources, can significantly impact project scheduling.
Why Identify Resource Availability?
Understanding the availability of your team members is essential for several reasons:
- Realistic Scheduling: It allows you to create a project timeline that aligns with the actual availability of resources. This ensures that tasks are allocated an appropriate amount of time, preventing overloading team members.
- Conflict Resolution: Identifying potential conflicts in resource availability helps you address them proactively. If team members are engaged in multiple projects simultaneously, you can adjust timelines or redistribute tasks to avoid bottlenecks.
- Effective Resource Allocation: It enables you to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that the right people are assigned to the right tasks at the right time.
Resource Availability in the e-Commerce Project Example
Task: Develop Back-End Functionality
Estimated Duration: 20 days
Resource Availability Consideration
- Team members’ schedules: Evaluate when the development team can work on back-end development.
- Concurrent projects: Determine if team members are involved in other projects that may affect their availability.
- Workload distribution: Ensure the workload is evenly distributed among developers to prevent overcommitment.
Revised Task Duration: 25 days
In this scenario, the project timeline accurately reflects the team’s capacity by identifying resource availability and adjusting the task duration to 25 days. This approach prevents resource overload, promotes effective project execution, and contributes to the successful creation of the e-commerce website.
Create Your Timeline
Now comes the main part—creating your project management timeline for the e-commerce website development project. This is where you’ll visually map out all the tasks, adjust their durations to match the allotted timeframes, and add essential milestones to ensure a smooth project flow. Behold your completed project management timeline!
Pro Tips for Building Your E-commerce Project Timeline
- Set Start and End Dates: Before diving into task details, establish the project’s start and end dates. This foundational step helps create a preliminary project schedule.
- Choose Line or Block Timeline: Decide whether a line or block timeline suits your project best. A basic line timeline highlights key milestones, while a block timeline visualizes team-specific task progress.
- Label Timelines: Label your project timeline based on the appropriate time units—seconds, hours, days, weeks, or even years.
- Stack Multiple Timelines: If needed, stack multiple timelines, ensuring that labels appear on the bottom timeline for clarity.
- Color-Coding: Organize your project by color-coding different timelines or rows. This practice helps keep the project organized and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Interval Adjustments: When adjusting intervals, do so only in complete increments to maintain accuracy and consistency.
By creating a project management timeline tailored to your e-Commerce project, you’ll have a visual roadmap that streamlines project execution, ensures timely completion, and keeps everyone aligned with project goals.
Source: invensislearning.com