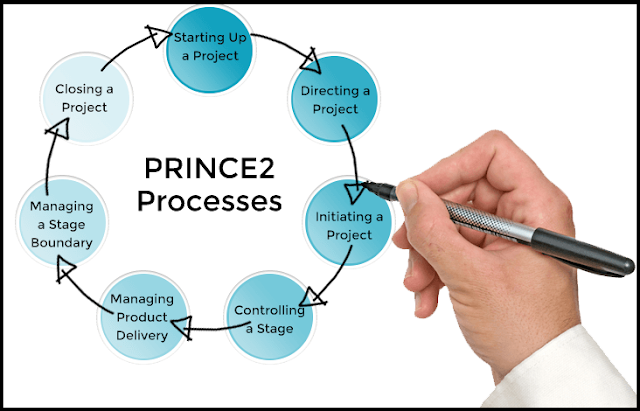
Processes: 7 processes of PRINCE2 describe obligations. In easy words- these course of informing who will do what and when. Seven processes of PRINCE2 are:
1. Starting up a project
2. Initialization of a project
3. Direction of a project
4. Controlling a stage
5. Management of product delivery
6. Management of stage boundaries
7. Closures of a project
Starting up a Project (SU)
The first PRINCE2 process is Starting up a Project (SU), which takes place before the project, is designed to assure the key stakeholders that it will be a reasonable and rewarding undertaking. The trigger for SU is the project mandate, a document provided by the commissioning organization (often corporate/program management) to explain the reasons and objectives for the project, as well as, in some cases, high-level estimations of time and cost.
The SU process is carried out once on each project and is oriented towards gaining the authorization necessary for initiating the project. This authorization constitutes the trigger for Initiating a Project (IP), which is the second PRINCE2 process.
Initiating a Project (IP)
This Course of entails planning intimately. The output doc of this course of is PID - Venture Initiation Doc.
IP involves these activities:
1. Manufacturing of 4 administration methods: the challenge's Danger, High quality, Configuration, and Communication Administration Methods.
2. Doc and make sure that a suitable Enterprise Case exists for the undertaking
3. Establishing challenge controls.
4. Organizing mission records data.
5. Assembling an Undertaking Initiation Doc (PID).
Directing a Project (DP)
This PRINCE2 course of runs from the beginning of the challenge till its closure. This course of is aimed at the Mission Board. The Mission Board manages and displays through experiences and controls via numerous choice factors.
DP involves these activities:
1. Authorizing initiation.
2. Authorizing a project.
3. Allowing a stage or exception plan.
4. Advert hot route (monitoring progress, offering recommendation and steerage, reacting to exception conditions)
5. Mission closure actions.
Controlling a Stage (CS)
This PRINCE2 course of describes the monitoring and management actions of the Undertaking Supervisor. This course of consists of the way in which through which work packages are authorized and obtained.
CS involves these activities:
1. Authorizing work package deal (Work to be performed).
2. Assessing progress.
3. Capturing and inspecting venture points.
4. Reviewing stage standing.
5. Reporting highlights.
6. Taking corrective motion.
7. Escalating venture points.
8. Receiving an accomplished work bundle.
Managing Product Delivery (MP)
The PRINCE2 project management methodology operates on the assumption that the project is based upon a customer/supplier environment. The process Managing Product Delivery (MP) describes the tasks and responsibilities of the Team Manager in their role as supplier, that is, in accomplishing the goals of a Work Package
MP involves these activities:
1. Accepting a work package
2. Executing a work package
3. Delivering a work package
Managing a Stage Boundary (SB)
To create normal control points for the Project Board, a PRINCE2 project must be divided into management stages, at the boundaries of which the Project Board reviews project progress and decides whether or not to commit further resources to the project.
The purpose of the Managing a Stage Boundary (SB) process is for the Project Manager to prepare for the next management stage, by providing the Project Board with relevant and accurate information for making a decision about the project’s continued viability. It Includes creating a Stage Plan (or an Exception Plan) and updating the Project Initiation Documentation.
SB involves these activities:
1. Plan the next stage
2. Update the project plan
3. Update the business case
4. Report the stage end or produce an exception plan
Closing a Project (CP)
A PRINCE2 project does not simply end upon fulfillment of the project objectives (described in the Project Initiation Documentation). The Project Manager is also responsible for making sure of the following:
1. Project products are delivered and approved;
2. Necessary ongoing maintenance is in place for the products that the project has created;
3. Benefits reviews have been either satisfactorily conducted or planned;
4. Preparations have been carried out to deal with unresolved issues and risks following the project.




0 comments:
Post a Comment